Like every year, RSAC was a magnificent show. We had a lot of people attending the SentinelOne booth who wanted to get more familiar with our solution. We had four demo stations in the booth, in which we demonstrated real-world use-cases where SentinelOne solution is truly valuable. One of the demos was really a jaw dropper. We demonstrated detection of ransomware and a rollback to a previously known healthy state of the operating system. Several booth visitors, who experienced successful ransomware attacks (some resulted in paying the ransom, others with data loss) were enthusiastic about what they have just seen.
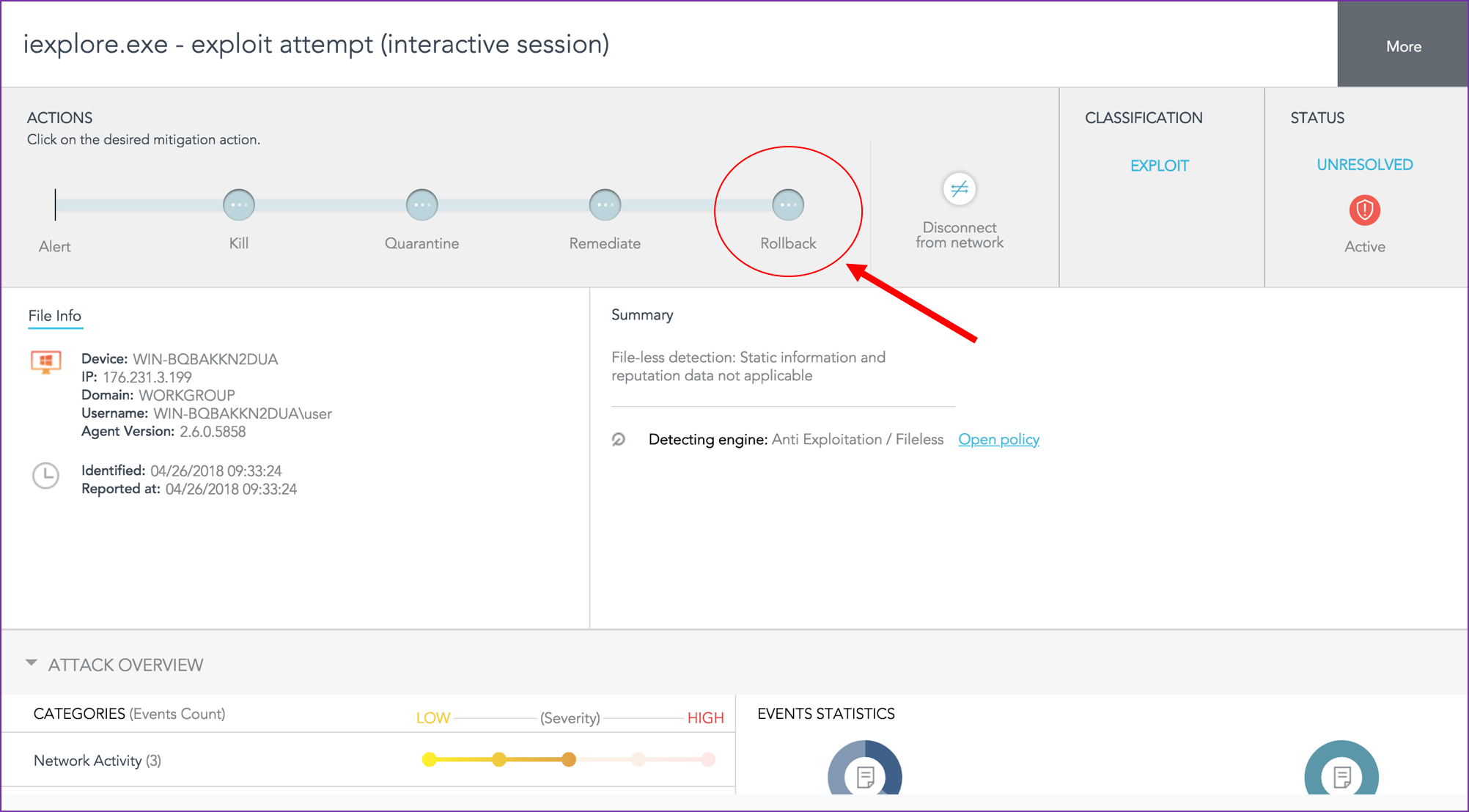
In this post, we will review the demo environment and the set of public tools that we used to establish it. A short video clip is brought at the end, demonstrating the attack flow and the rollback mitigation.
The demo consists of two VMs which are set-up to show a typical Metasploit browser exploit attack.
Attacker VM
This is a simple Kali Linux machine which is set to automatically start the Browser Autopwn 2, an auxiliary module that is provided by Metasploit. The idea behind this module is that it creates a web server which serves different types of exploits for Firefox, Internet Explorer, Adobe Flash, and more. Using “Browser Autopwn 2”, one can easily test browser vulnerabilities. By default, “Browser Autopwn 2” is delivered with 21 exploits. When a browser connects to the web server, the module tries several exploits until it finds a vulnerability. In our demo, the Victim VM is vulnerable to adobe_flash_avm. This exploit, from 2014, exploits a vulnerability in Adobe Flash Player ActiveX component, which results in a remote code execution. This is admittedly an old exploit, and many systems are now patched, but this type of attack is still common.
Once the exploit succeeds, it downloads a TeslaCrypt payload and runs it on the victim machine. TeslaCrypt was detected in February 2015. Originally, it targeted computer game data such as games saves, player profiles, etc. Newer variants of TeslaCrypt were not focused on game-related data and also encrypted JPEG, PDF, and other file types. In our demo, all images residing on the victim machine get encrypted.
Victim VM
This machine runs Internet Explorer with vulnerable version of Shockwave Flash (CVE 2014-0497). When the user browses to the Attacker VM, the “Browser AutoPwn 2” module finds the suitable exploit for the browser, sends the ransomware payload, and executes it. The ransomware then encrypts the images and leaves a ransom note on the screen.
Demo
In this demo we set the policy to Detect/Detect, which means that the agent only detects threats or suspicious behavior (instead of blocking). The reason for that is to let the ransomware encrypt the images, so we can demonstrate the rollback capability. Our recommendation is to set the policy to Protect/Detect, which means that threats such as the ones presented in this demo, will be blocked before something bad happens. Therefore, the rollback option will be used only in rare use-cases as another layer of protection.
Want to see more of these? To evaluate the SentinelOne Endpoint Protection Platform for yourself, please send us an email at [email protected] or use our Request a Demo form and we’d be happy to show you why we are the top-rated endpoint solution in the industry.