Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a sophisticated scam targeting businesses to steal money or sensitive information. This guide explores how BEC attacks are executed, their impact on organizations, and effective prevention strategies.
Learn about the importance of employee training and awareness in combating BEC threats. Understanding BEC is crucial for organizations to protect their financial assets and sensitive data.
 What is BEC (Business Email Compromise)?
What is BEC (Business Email Compromise)?
Most often, Business Email Compromise begins with a compromised or spoofed email account.
Under the guise of a trusted vendor, or a company executive, scammers typically use stolen or false credentials to trick employees into giving up financial authorization or confidential information permissions. This may include making wire transfers to an illegitimate third party. Falsely believing the wire transfer instructions come from a high-ranking member of leadership, employees unknowingly commit fraud by sending funds directly to the attacker.
Once the money leaves corporate accounts, it’s gone for good. In many cases, the funds end up in overseas bank accounts, which are used by the criminals to receive the funds without being traced.
A form of social engineering, BEC requires attackers to convince the targeted employees that their request for funds is legitimate to push the wire transfer through. Attackers may spend time enacting reconnaissance before executing a BEC attack to ensure they have enough information about the vendor or executive they are impersonating as well as the employee they’re targeting with the request.
Social engineering tactics are also popular in cases where attackers steal passwords and compromise legitimate accounts, rather than spoofing them.
Business Email Compromise Example
The first part of a BEC typically involves either a targeted phishing (aka spear phishing) attack or credential theft through keyloggers. For example, a C-suite executive may be targeted with a phishing attack that installs a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) to harvest credentials and other useful business information.
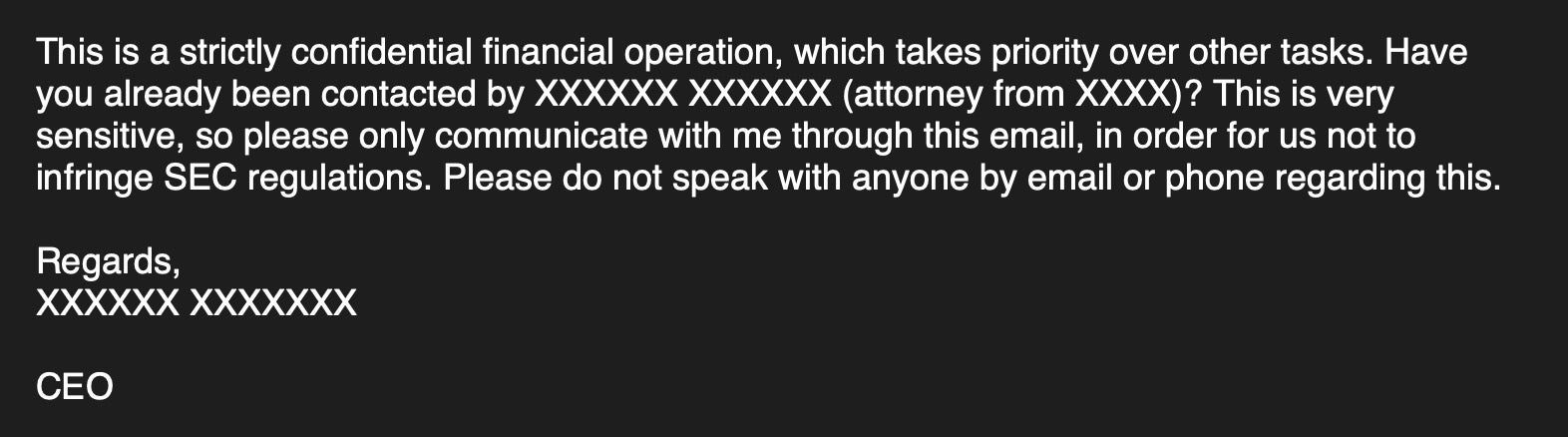
After that, the account may be used to instruct other employees to complete a wire transfer request from a fake supplier. It is important to note that these emails often employ a tone of extreme urgency and urge the targeted employee to keep the transaction confidential. A spoofed or hacked account of a C-suite executive may be used to send an internal email that reads something like the following:
How Much Do Business Email Compromises Cost?
Statistics collected by the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Internet Crime Complaint Center revealed a total of 241,206 domestic and international incidents of BEC between 2013 and 2021. This totaled to an exposed loss of over $43 billion.
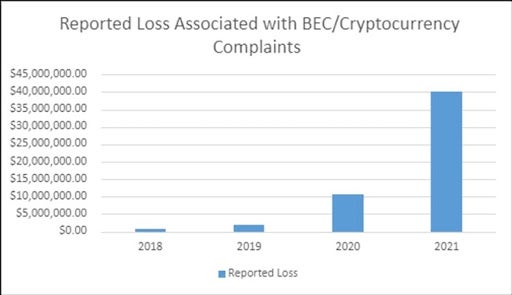
The PSA highlighted that, “This increase can be partly attributed to the restrictions placed on normal business practices during the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused more workplaces and individuals to conduct routine business virtually.” The FBI also noted an increased number of BEC complaints involving cryptocurrency.
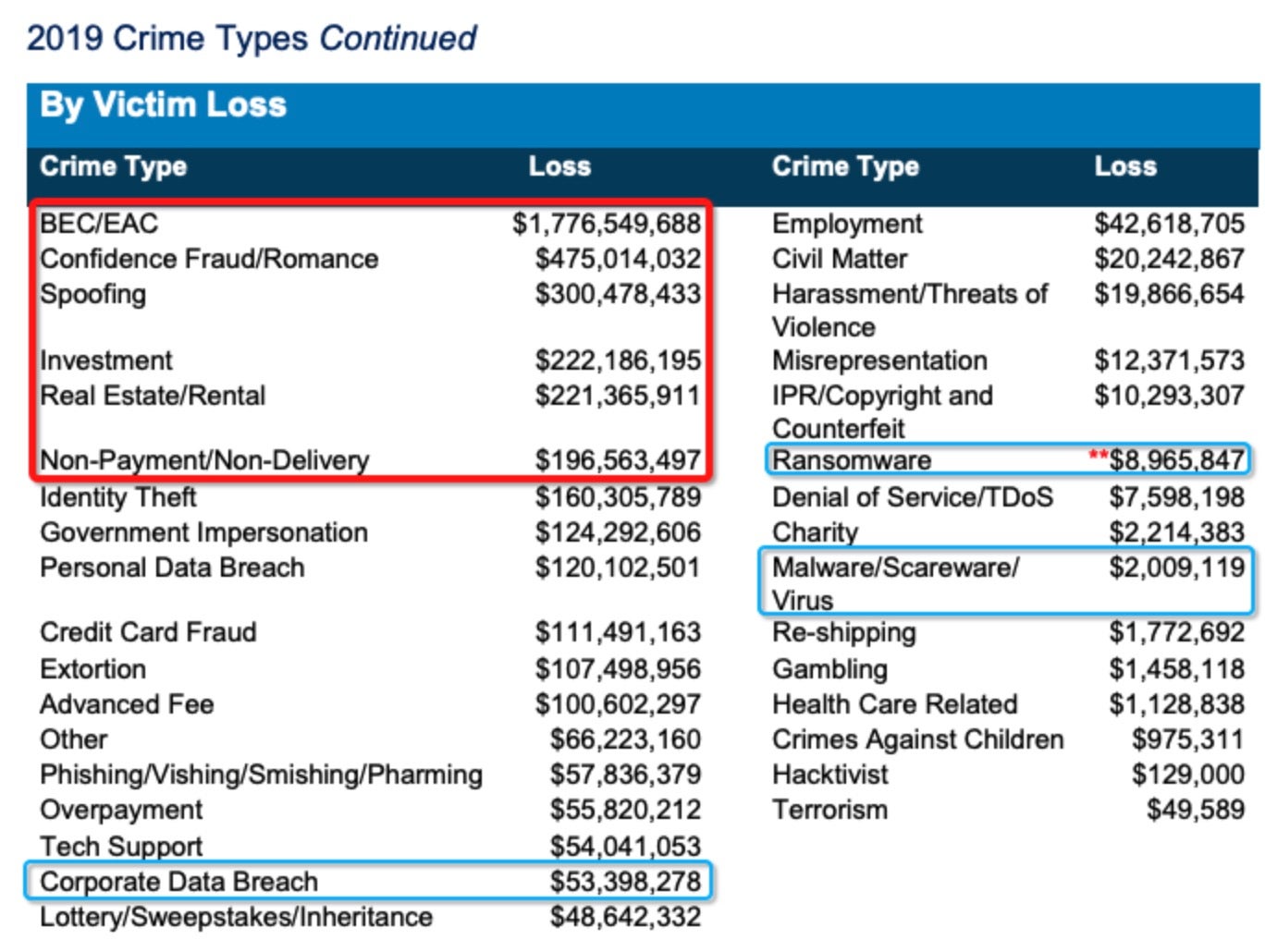
BEC was still an issue before 2020. Stats suggest that losses due to ransomware averaged out at around $4,400 per incident and totaled just shy of $9 million in the U.S. in 2019. In contrast, losses due to BEC were around 17 times higher, at $75,000 per incident, and amounted to a total financial loss north of $1.7 billion for the same period.
Of all financial losses due to internet crime recorded by the FBI during 2019 – in sum, around $3.5 billion worth – BEC accounted for around 50% of the total:
 How Business Email Compromise Scams Work
How Business Email Compromise Scams Work
A typical business email compromise scam follows a timeline as listed below:
1. Target Identification
The attacker finds a target and collects as much information as they can find on them. This can be done by exporting information available online to develop a profile on the company and its executives.
2. Contact
Spear phishing emails or phone calls target the victim’s company (typically members of the financial department). The attacker exchanges a series of emails with the targeted employee in order to build a trusted relationship. They’ll often pretend to be trusted vendors or employees inquiring about payments or sensitive data.
3. Fund Request
Once trust has been established, the scammer makes the request for funds. This doesn’t raise any red flags right away for the employee because they truly believe this is a legitimate transaction. In some cases, the attacker might even return and request another transfer.

What to Do After a Business Email Compromise Scam
As soon as an employee suspects they were targeted, there are a few steps to take to safeguard the rest of the company.
- Alert the company IT department of the incident to secure the email account that was compromised
- Reset or change passwords for all compromised accounts
- Contact the financial institution that the funds were sent from and request a recall or reversal
- Report the crime to the FBI internet crime complaint center
- Continuously educate all employees and managers with how to stay safe from any further BEC efforts.
Luckily, there are simple, effective ways to get ahead of scammers leveraging Business Email Compromise.
How to Defend Against BEC Attacks
Business Email Compromise revolves around three interrelated factors: email, people, and wire transfers. To protect against BEC attacks, organizations can prioritize security for each of those elements as part of a layered, defense-in-depth approach.
Confirm Wire Transfers
Companies should confirm wire transfer requests by some medium other than email. They might verify the request via a phone call through:
- A known legitimate company number (not one provided in the email),
- An authorized workplace communication channel, or
- Face-to-face in person or via teleconferencing software.
It is best practice for organizations to also implement a secondary confirmation policy for wire transfers. Employees should be suspicious of demands that do not initiate communication through any medium other than email (which attackers often suggest).
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Although not immune to attack, enabling multi-factor identification (MFA) for email accounts can greatly help. MFA, sometimes referred to as two-factor authentication (2FA), can prevent the majority of account takeover attempts by simply requiring an additional method for verifying a user’s identity.
Biometrics or hardware security keys like Yubikey are another alternative to implementing MFA.
Detect Malicious Emails
Email has long proven to be the malicious actor’s best friend. It’s been estimated that anywhere between 80% – 95% of all enterprise attacks propagate through email, so having a strategy to protect users against malicious emails is an important pillar of defense.
Aside from the actual textual content of an email, there are two main technical risks associated with emails in general: malicious attachments and links.
Manage Malicious Attachments
In Business Email Compromises, attackers may use attachments to run executable code that can deploy a RAT to install keyloggers, backdoors, etc. These and other post-exploitation tools are used by attackers to steal credentials and useful data like contacts and previous email correspondence.
BEC scammers typically spend some time profiling their victims in order to craft content that’s as convincing as possible, increasing the success of the social engineering aspect of the scam. For that reason, it’s important to look at a range of options for preventing attachments from executing code. Attachment filtering can be used in a number of ways to help mitigate code execution. For example, email scanning software could be used to change file formats of attachments so that they cannot execute hidden code.
While this may be effective to a certain extent, it can also prevent users from carrying out ordinary business tasks with documents that need to be edited or returned to their original format. Given that impact, user resistance could be high.
A better solution would involve content disarm and reconstruction (CDR), which deconstructs the attachment and removes harmful content. This is both highly effective and meets low user resistance since the process is transparent at the user level.
Best Practices for Macros, Archives, and Whitelists
Protecting against BEC will also include putting defenses in place for macros, archives, and whitelists. Here are some best practices users can follow:
- Disable or restrict macros as much as possible: Many attacks make use of Microsoft Office’s VBA scripting language to call out to C2 servers and download malicious payloads.
- Ensure that email scanning software deals with archives properly: Compressed files can bypass some unsophisticated scanning engines if they do not decompress files fully. Attackers have been known to append archive files to other files like images which some security software might overlook.
- Be careful with whitelisting files by extension: Attackers try to bypass whitelisting rules by renaming executable files with non-executable file extensions. If users do whitelist attachments, it’s recommended to use a policy that whitelists by file typing – scanning the file to examine its format – to avoid the easiest of bypasses.
Managing Links and Sender Verification
To protect against emails containing malicious links, some organizations defang hyperlinks in emails so that they’re unclickable. The user must copy and paste the link into a browser instead; a conscious process that provides an opportunity for users to pause and consider what they’re doing.
The issue again is that whenever security impacts productivity and convenience, this can result in some user resistance. This security measure has twin drawbacks of being both inconvenient and fallible: the delay can be frustrating, and introducing the delay still does not guarantee the user will not visit the link.
Another strategy to consider is sender verification, through authentication methods such as DMARC and SPF/DKIM. These methods can help flag fake sender identities like spoofed accounts, but they may not help in cases where the account belongs to a legitimate member of an organization that’s been compromised by an attacker.
Finally, it is important to protect against both malicious attachments and malicious links by arming all endpoints with an AI-driven security solution that can detect and block malicious code as it attempts to execute regardless of its origin: file or fileless and link or macro.
 Get Deeper Threat Intelligence
Get Deeper Threat Intelligence
See how the SentinelOne threat-hunting service WatchTower can surface greater insights and help you outpace attacks.
Learn MoreStay Protected with SentinelOne
While it’s challenging to prevent a threat actor from attempting an attack, it is possible to detect an attack before it can spread deep within a network.
An autonomous security solution like SentinelOne will not only detect BEC attacks as they happen, but also ensure that attempts to install RATs, keyloggers, and other malware are stopped in their tracks.
While Business Email Compromise scams target the “weakest link” – busy staff trying their best to be productive – each step organizations can take to prevent and detect these cybersecurity threats will make a difference.
If you would like to see how SentinelOne’s Singularity platform can protect your enterprise from email-based cybersecurity attacks, request a free demo today.
Like this article? Follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, YouTube or Facebook to see the content we post.
Read more about Cyber Security
- RSAC 2020 Kicks Off with SentinelOne’s Singularity Platform
- What is Hacktivism? And Why Should Enterprise Care?
- Worried Whether Your Mac Can Get A Virus? Let’s Talk Facts
- Cyber Insurance & Information Security | Is InfoSec’s Criticism of Cyber Insurance Fair?
- Defeating Ransomware | Outflanking Attackers Through Public-Private Cooperation
- From Storage to SaaS Cybersecurity: The Why
- My Hospital Caught a Virus | How Healthcare Is Sick With Cyber
Business Email Compromise FAQs
Business Email Compromise is a type of cyber attack where criminals spoof or hack into business email accounts to trick employees into transferring money or sharing sensitive data. They often impersonate executives, suppliers, or partners, using carefully crafted emails to create urgency and bypass normal security controls.
BEC attackers usually focus on organizations with finance departments, executives, or HR teams. Small and large companies alike can be victims. Attackers target employees authorized to approve payments, confidential information, or vendors to manipulate valid transactions for fraud.
Attackers either spoof or gain access to a trusted email account, then send fake invoices, fund transfer requests, or sensitive info queries. They create urgency or secrecy to pressure the recipient into acting quickly, often bypassing verification. These emails look legitimate, increasing the chance of success.
Unusual requests for wire transfers or sensitive data, especially outside normal business hours. Emails urging secrecy or quick action. Slight changes in email addresses or domains, misspelled names, or unfamiliar wiring instructions. Requests inconsistent with established procedures are red flags.
MFA helps by blocking unauthorized account access but isn’t a complete shield. Many BEC scams rely on spoofing or social engineering, which don’t require compromised credentials. Combine MFA with user training, email filtering, and transaction verification to reduce risk effectively.
Common types include CEO fraud (impersonating executives), invoice fraud (fake supplier invoices), account compromise (hacked email accounts), and attorney impersonation. Each uses social engineering tactics to trick employees into unauthorized actions, often with financial losses.
Require multi-factor authentication and strong passwords for email accounts. Train employees on spotting phishing and social engineering. Implement strict payment verification processes like callbacks. Use advanced email filtering and anti-spoofing technologies like DMARC. Regularly audit email and financial workflows for anomalies.
Immediately change affected account passwords and revoke session tokens. Verify if any payments were sent and, if possible, recall or block transactions. Notify the finance team and relevant authorities like law enforcement. Conduct a full investigation, update security controls, and retune training to prevent repeats.


