The Good | Authorities Crack Down on Identity, Romance Baiting & Phishing Schemes
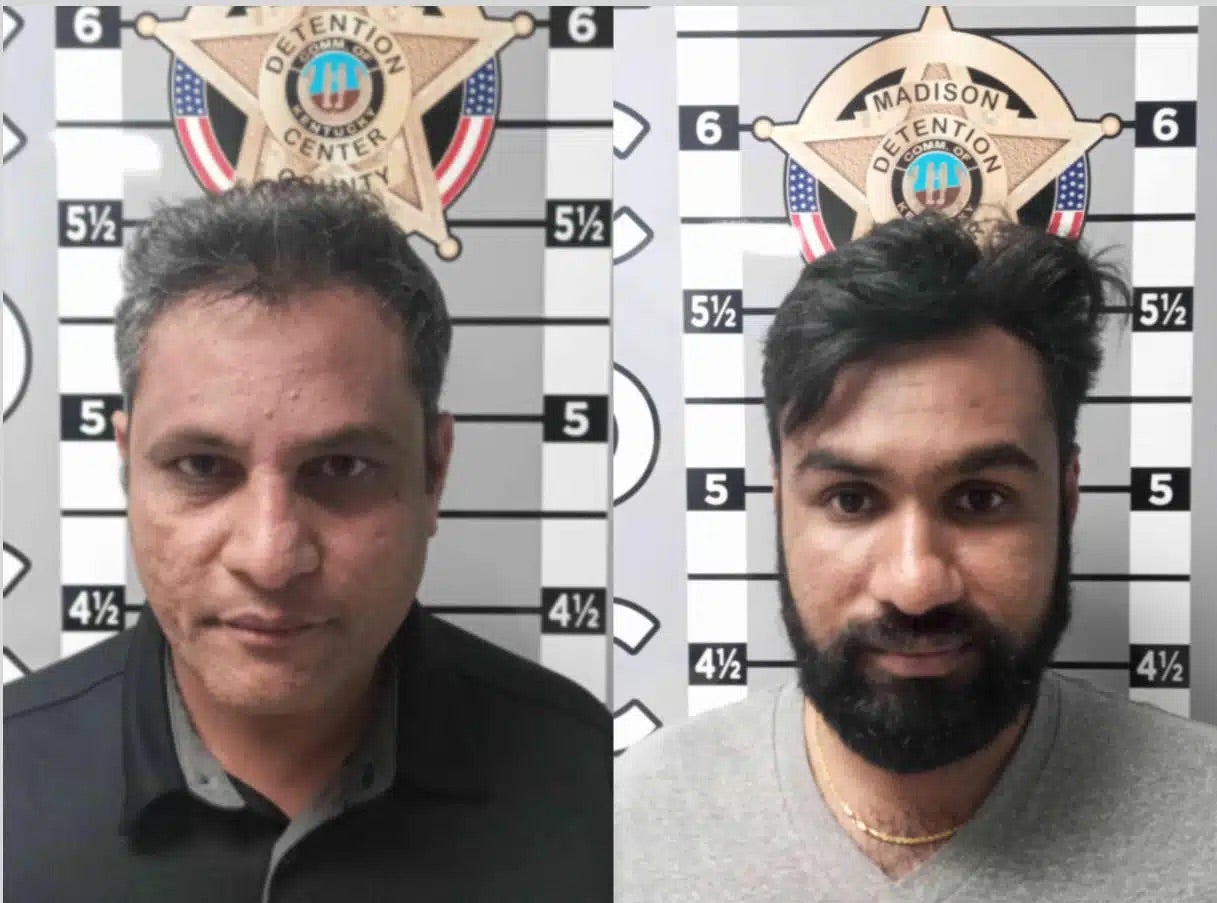
Two individuals have been indicted for a years-long scheme that used stolen identities from 3,000 victims to siphon $3 million from sportsbooks. Amitoj Kapoor and Siddharth Lillaney allegedly bought personally identifying information (PII) on dark markets and Telegram, opened thousands of fake accounts on FanDuel, DraftKings, and BetMGM, and harvested new-user bonuses.
The pair allegedly used background-check services to pass verification checks and cashed out winnings via prepaid cards into controlled accounts. Prosecutors have filed for charges of fraud, identity theft, and money laundering charges carrying several decades in prison.

In further crackdowns on fraudulent schemes, a dual Chinese and St. Kitts & Nevis fugitive has been sentenced in absentia to 20 years for orchestrating a romance baiting crypto scam worth over $73 million.
Daren Li built trust with victims via messaging and dating apps before steering them into fake investments, then laundering the stolen funds through shell companies, U.S. bank accounts, and cryptocurrency platforms using assets like Tether. Arrested in 2024, Li fled two months ago while awaiting sentencing. Investigators tied the syndicate to hundreds of millions in laundered crypto and wider global losses.
Police in the Netherlands have arrested a man for allegedly selling access to JokerOTP, a phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) tool that intercepts one-time passwords to hijack accounts. The suspect, the third arrest in a three-year long probe, allegedly marketed licenses via Telegram to criminals who used automated calls to impersonate trusted companies and trick victims into revealing codes and sensitive data.
Authorities say the service enabled over 28,000 attacks across 13 countries, causing roughly $10 million in losses and targeting accounts on PayPal, Venmo, Coinbase, and Apple. While investigations continue, dozens of JokerOTP bot buyers have already been identified and face prosecution in due time.
The Bad | APT Groups Weaponize Google Gemini in All Stages of Cyber Kill Chain
State-backed hackers and cybercriminals are increasingly exploiting Google’s Gemini AI to streamline their attacks from initial reconnaissance to post-compromise operations. According to new research, actors linked to China, Iran, North Korea, and Russia used the model for target profiling, phishing lure generation, translation, coding, vulnerability testing, command-and-control development, and data exfiltration.
Some operatives even posed as cybersecurity experts to trick the AI tool into producing detailed exploitation plans, including remote code execution (RCE) and web-application (WAF) firewall bypass techniques against specific targets in the U.S.
Iranian-linked threat group APT42 leveraged the model to accelerate social engineering campaigns and tailor malicious tools, while others integrated AI-assisted capabilities into malware such as a CoinBait phishing kit and HonestCue malware launcher. Criminal groups also used generative AI in ClickFix campaigns that delivered infostealing malware through deceptive troubleshooting ads. Researchers also noted signs of AI-generated code in malware artifacts, indicating that generative platforms are already shaping attacker toolchains.
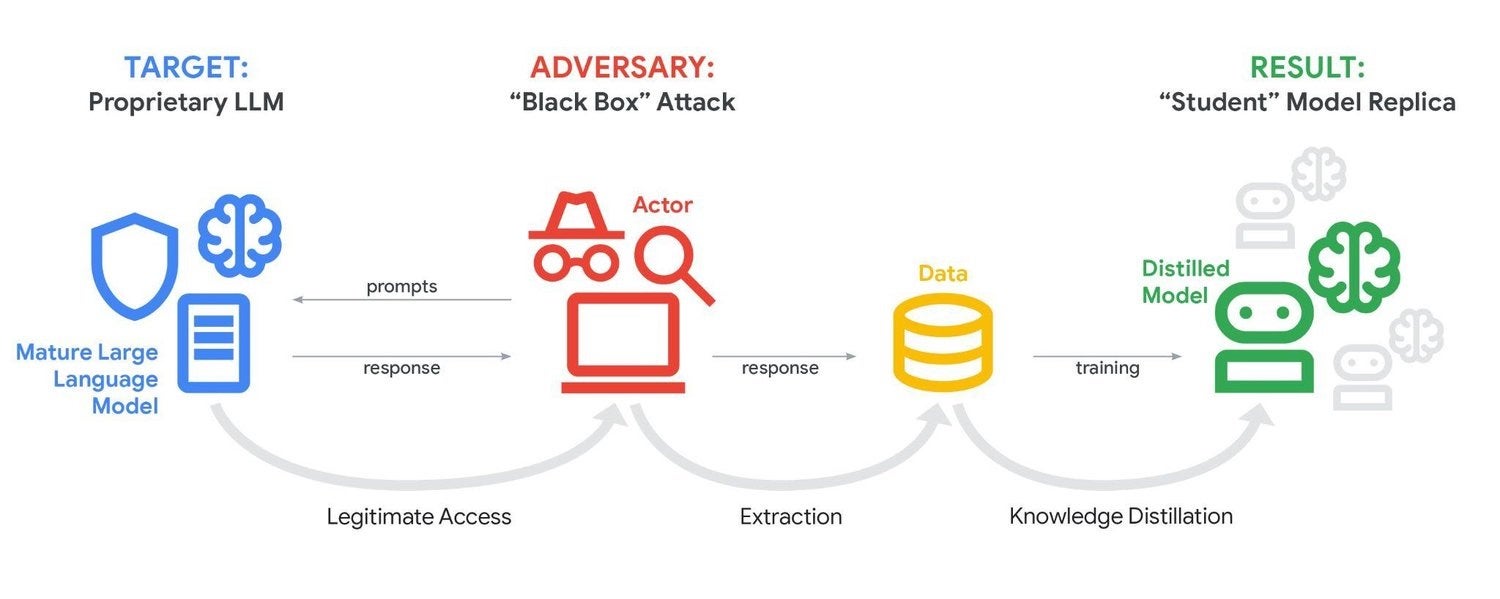
Beyond direct abuse, the report observed attempts to extract and replicate Gemini itself through large-scale querying and “knowledge distillation” techniques, in which actors use data from one model to train fresh, more advanced ones. While this mostly threatens AI vendors’ intellectual property, it could also eventually affect end users of the tool as AI-as-a-Service continues to rise.
Google says it has disabled the malicious accounts and continues to harden its defenses to limit misuse and make it more difficult to exploit. However, researchers warn that AI integration will likely accelerate threat actor capabilities across cybercrime ecosystems, lowering barriers to entry and increasing the speed, scale, and sophistication of future attacks.
The Ugly | China-Based Actors Hit Major Singaporean Telcos in Ongoing Espionage Campaign
Singapore’s Cyber Security Agency (CSA) revealed this week that the China-linked threat actor UNC3886 has targeted each of the country’s four largest telecommunications (teleco) providers – Singtel, StarHub, M1, and Simba Telecom – at least once last year.
Using sophisticated tools and zero-day exploits, the APT gained limited access to critical systems. While it did not disrupt services or exfiltrate sensitive customer data, rootkits helped UNC3886 maintain stealthy persistence while siphoning technical data to support operational objectives.

CSA has since responded with “Operation Cyber Guardian”, an 11-month long campaign bringing together over 100 investigators across six government agencies to support. Authorities closed access points in the teleco networks, expanded monitoring, and blocked attempts to pivot into banking, transport, or healthcare networks. The agency also emphasized that while UNC3886’s intrusions were deliberate and well-planned, mitigation measures were able to prevent major disruption.
Active since at least 2022, the PRC-based actor is known to target virtualization technologies and edge devices, often fabricating scenarios to test and exploit vulnerabilities without triggering alerts. Previous activity included targeting telecommunications networks in the U.S. and Canada with the goal of developing cross-border espionage capabilities.
CSA described UNC3886 as “an advanced persistent threat with deep capabilities”, noting that the recent campaign demonstrates the ongoing risk to critical national infrastructure. The agency stressed the importance of cyber defense readiness, stating that rapid remediation, monitoring, and coordinated response measures continue to be key to containing the attacks and protecting Singapore’s teleco sector.