Kubernetes is an open-source orchestration platform for containers. It abstracts the underlying infrastructure and provides a platform for automating the deployment, scaling and management of containerized applications and services. Essentially Kubernetes enables developers to define the desired state using declarative configuration files, which Kubernetes then automatically manages and maintains. This guide explores the key features and benefits of Kubernetes, including its architecture and ecosystem.
Learn how Kubernetes enhances application reliability and scalability, and discover best practices for implementing Kubernetes in your organization. Understanding Kubernetes is crucial for leveraging container orchestration effectively.

In many ways, containers are very similar to virtual machines; however, the biggest difference is that they are more relaxed in isolation properties, allowing sharing of the operating system across applications. Containers are lightweight (especially compared to VMs), have their own file system, and share CPU, memory, and process space.
Containers are an excellent way to bundle and run your applications but they require management. Kubernetes is the de-facto standard for container orchestration and management. It provides a comprehensive platform for deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications.
Why Use Kubernetes?
Here are some reasons why you need Kubernetes:
- Scalability and High Availability – Kubernetes make it easy to scale up or down your application as needed. It enables high availability by automatically restarting containers that fail, rescheduling containers on other nodes if a node goes down, and replicating containers to ensure that your application is always available.
- Declarative – Configuration Kubernetes uses a declarative approach to configuration. You describe the desired state of your application, and Kubernetes takes care of the rest. This means you don’t have to worry about the underlying infrastructure and can focus on your application’s logic.
- Automation – Kubernetes automates many tasks, such as rolling out updates, scaling, and self-healing. It eliminates manual intervention, reducing the likelihood of human error and freeing up your team’s time.
- Portability – Kubernetes is a portable platform that runs on any cloud, on-premises, or hybrid environment. It allows you to move your applications seamlessly between different environments without changing the underlying infrastructure.
- Ecosystem – Kubernetes has a large and rapidly growing ecosystem with many tools and services available.
- Resilience – Kubernetes provides built-in mechanisms for ensuring that applications are always available, even if a container or node fails. It can automatically restart containers, migrate them to healthy nodes, and ensure that applications run reliably.
- Flexibility – Kubernetes provides a flexible platform for deploying and managing applications. It supports a wide range of container runtimes, including Docker and containers, and allows you to use storage, networking, and monitoring tools.
What are Containers?
Before we dive deeper into Kubernetes, let’s first understand what containers are. Containers are lightweight and portable executable units that package application code and all its dependencies in a single bundle. They provide a consistent runtime environment, regardless of the underlying infrastructure, making moving applications between different environments easier.
How Does Kubernetes Work?
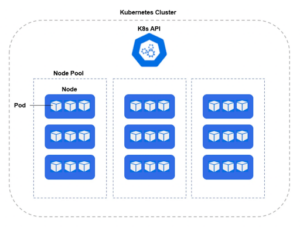
Kubernetes is deployed in a cluster, whereas the physical server or virtual machines which are part of the cluster are known as worker nodes. Each worker node operates a number of pods, which are a logical grouping of 1 or more containers running within each pod.
Kubernetes uses a set of APIs to communicate with the underlying infrastructure, such as container runtime, storage, and networking. Some of the core components of Kubernetes include:
- API Server – The control plane of Kubernetes. It exposes the Kubernetes API, which allows clients to communicate with the Kubernetes cluster. The API server is responsible for authenticating and authorizing client requests, validating and processing API objects, and updating the state of the cluster.
- Controller Manager – Controllers (also called kube-controller-manager) are responsible for maintaining the desired state of your application. They ensure that the right number of pods are running and that they are healthy and up-to-date. The controller manager is responsible for maintaining the desired state of the cluster. It watches the state of the cluster through the API server and compares it to the desired state specified in the Kubernetes objects. If there is a difference between the current and desired state, the controller manager takes appropriate actions to bring the cluster back to the desired state.
- Scheduler – Responsible for scheduling workloads on the cluster’s worker nodes. It watches for new workloads that need to be scheduled and selects an appropriate node to run the workload based on the resource requirements and availability of the node.
- Kubernetes Services – API objects that that enable exposure for one or more cluster Pods to the network either within your cluster or externally.
- etcd – The distributed key-value store for the configuration data of a cluster. It provides a consistent and reliable way to store and retrieve configuration data across the cluster.
Several features relevant for security professionals to be aware of:
- Namespace – A logical construct which allows isolation of resources within the cluster. A namespace separates users, apps, and resources into a specific scope.
- SecurityContext – defines privileges and capabilities for individual pods and containers.
- Helm Chart – A manifest of YAML files for deployments, services, secrets, and config maps to configure your Kubernetes deployment.
- DaemonSet – a fundamental controller that ensures a specific pod runs on every node, or a targeted subset of nodes, within a cluster. This is critical for deploying system-level services that require consistent operation across the entire cluster. Examples of such services include log collectors, monitoring agents, and network management tools. The DaemonSet controller automates the management of these pods, creating them on newly added nodes and removing them when nodes are removed, ensuring full observability, security, and network management across the infrastructure.
Kubernetes Deployment
While Kubernetes can be deployed across the spectrum of hybrid cloud, the majority of K8s implementations are managed via Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) tooling, such as Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Google GCP’s Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) or Microsoft Azure’s Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). By using these Kubernetes-as-a-service tools, teams can focus on building and deploying, while the Cloud Service Provider (CSP) curates and updates core aspects of the K8s services. As always with the Cloud Service Providers, there is still a Share Model of Responsibility to consider when it comes to security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Kubernetes offers numerous benefits for managing containerized applications, security should always be a top concern for businesses. Singularity Cloud Security helps businesses stay protected against modern threats by offering both Proactive and Reactive Security controls for cloud and container environments.Singularity Cloud Workload Security is an agent-based security solution that provides autonomous runtime protection and forensic telemetry collection across all cloud compute and container, regardless of lifespan.Singularity Cloud Native Security is an agentless CNAPP for visibility and security controls over both build and runtime environments. Security for templates, images, hosts, identities, privileges, permissions, and configurations associated.
By incorporating Singularity Cloud Security into their Kubernetes environments, businesses can add an extra layer of security to their containerized applications and protect themselves from cyber threats.
As a result, customers can rest assured that their applications and data are safe and secure, allowing them to focus on achieving their business objectives without worrying about cybersecurity issues.
See SentinelOne in Action
Discover how AI-powered cloud security can protect your organization in a one-on-one demo with a SentinelOne product expert.
Get a DemoKubernetes FAQs
Kubernetes is an open-source platform that automates deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications on clusters of servers. It ensures containers stay running, distributes load, and handles rollouts or rollbacks.
Originally built by Google, Kubernetes groups containers into logical units called Pods and uses a control plane to maintain the desired state of applications, making large-scale container operations reliable and repeatable.
A Kubernetes cluster has a control plane and worker nodes. The control plane includes kube-apiserver (the API frontend), etcd (a key-value store), kube-scheduler, and kube-controller-manager.
Worker nodes run kubelet (node agent), kube-proxy (networking), and a container runtime like containerd. Optional addons—DNS, dashboards, logging, and monitoring—extend functionality and aid operations.
A Deployment manages stateless Pods, ensuring a specified number run and updating them in a controlled way. A StatefulSet handles stateful applications by giving each Pod a stable identity and persistent storage, ideal for databases. A DaemonSet runs one Pod per node (or per selected nodes), guaranteeing that a copy of a service—like a log collector or node-agent—runs on every node.
On Linux or Windows, you can use kubeadm: install Docker or containerd, kubeadm, kubelet, and kubectl, then run kubeadm init (control plane) or kubeadm join (worker). For a local single-node cluster, Minikube installs a VM or container with a control plane and kubelet: minikube start sets up everything automatically. You then use kubectl to interact with your cluster.
kubectl is the command-line tool for Kubernetes. It sends REST API requests to the kube-apiserver, letting you create, inspect, update, or delete resources like Pods, Deployments, and Services. You can view logs (kubectl logs), exec into containers (kubectl exec), apply YAML manifests (kubectl apply -f), and troubleshoot clusters directly from your terminal.
Prometheus paired with Grafana offers metrics collection and visualization, tracking CPU, memory, and custom application data. Fluentd or Filebeat can forward container logs into Elasticsearch, then visualize them in Kibana. Other options include the Kubernetes Metrics Server for autoscaling, EFK (Elasticsearch-Fluentd-Kibana) stacks, and hosted services like Datadog or Sysdig.
SentinelOne deploys a lightweight Sentinel agent on each node as a DaemonSet, protecting live containers at runtime with static and behavioral AI. It supplements pre-production scans with real-time prevention, detection, and response for malware, fileless threats, and ransomware. The agent integrates into Singularity XDR for unified visibility and automated remediation.
Yes. SentinelOne’s Kubernetes Sentinel agent delivers runtime protection and EDR visibility for containerized workloads. It operates entirely in user space—no kernel modules—providing threat hunting, Storyline Active Response, and full forensic telemetry across all major Linux distributions and managed services like AWS EKS and Azure AKS.


