The Good | Europol Dismantles Global SIM-Box Fraud Network
Europol has dismantled a major cybercrime-as-a-service (CaaS) operation, codenamed SIMCARTEL, that powered over 3,200 fraud cases and caused at least €4.5 million in damages. The network operated 1,200 SIM-box devices containing some 40,000 SIM cards, enabling criminals to rent phone numbers registered to individuals in more than 80 countries. These were then used to create 49 million fraudulent online accounts for crimes including phishing, investment fraud, extortion, impersonation, and migrant smuggling.
The illegal service, run through gogetsms.com and apisim.com, worked by selling access to “fast and secure temporary” phone numbers marketed for anonymous communication and account verification. GoGetSMS also offered users a way to monetize their own SIM cards. However, reviews suggested it was a front for large-scale identity fraud, now exposed as one of Europe’s most extensive SIM-box schemes to date. Europol said the infrastructure was “technically highly sophisticated”, which allowed perpetrators worldwide to hide their identities while conducting telecom-based fraud.
After running coordinated raids across Austria, Estonia, Finland, and Latvia, police arrested seven suspects in total. They also seized five servers, the two websites, hundreds of thousands of SIM cards, €431,000 deposited in bank accounts, €266,000 in crypto, and four luxury vehicles. Both domains have been taken down and now display official law enforcement banners.

So far, authorities have linked the network to 1,700 fraud cases in Austria and 1,500 in Latvia, with combined losses adding up to nearly €5 million. Europol’s forensic analysis of the seized servers aims to identify customers of the illegal service.
The Bad | Jingle Thief Exploits Cloud Identities for Large-Scale Gift Card Fraud
A new report from security researchers details the activities of ‘Jingle Thief’, a financially motivated threat group that operates almost entirely in cloud environments to conduct large-scale gift card fraud. Active since at least 2021, the group targets retail and consumer services organizations through phishing and smishing campaigns designed to steal Microsoft 365 credentials.
Once inside, the attackers exploit cloud-based infrastructure to impersonate legitimate users, gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, and manipulate gift card issuance systems. With their campaigns focusing on mapping cloud networks, attackers can move laterally across accounts and avoid detection through stealthy tactics such as creating inbox rules, forwarding emails, and registering rogue authenticator apps to bypass MFA in M365.
Unlike traditional malware-driven attacks, Jingle Thief relies heavily on identity misuse, choosing to leverage stolen credentials instead of deploying custom payloads to blend in with normal user activity. This approach allows them to maintain access for many months while issuing or selling unauthorized gift cards for profit on gray markets.
Researchers also observed a major wave of Jingle Thief activity between April and May 2025, during which the group compromised more than 60 user accounts within a single organization. The attackers conducted extensive reconnaissance in SharePoint and OneDrive, searching for financial workflows, IT documentation, and virtual machine configurations, all tied to gift card systems.
Exploiting cloud identities rather than endpoints furthers the trend of cloud-based cybercrime, where phished credentials and identity abuse enable financially motivated actors to scale operations while remaining under the radar. Jungle Thief’s campaign is a reminder to prioritize identity-based monitoring and cloud-native security measures that provide full visibility and real-time detection.
The Ugly | PhantomCaptcha Spearphishing Targets Ukraine’s Relief Networks
SentinelLABS, together with the Digital Security Lab of Ukraine, have uncovered ‘PhantomCaptcha’, a single-day spearphishing campaign that targeted Ukrainian regional government administrations and humanitarian organizations such as the International Red Cross, UNICEF, the Norwegian Refugee Council, and other NGOs linked to war relief efforts.
Launched on October 8, 2025, the operation began with an impersonation of the Ukrainian President’s Office, distributing weaponized PDF attachments that redirected victims to a fake Zoom site (zoomconference[.]app). There, a fake Cloudflare CAPTCHA lured users into copying and pasting malicious PowerShell commands – a ClickFix technique designed to bypass traditional endpoint controls by tricking victims into executing the malware themselves.
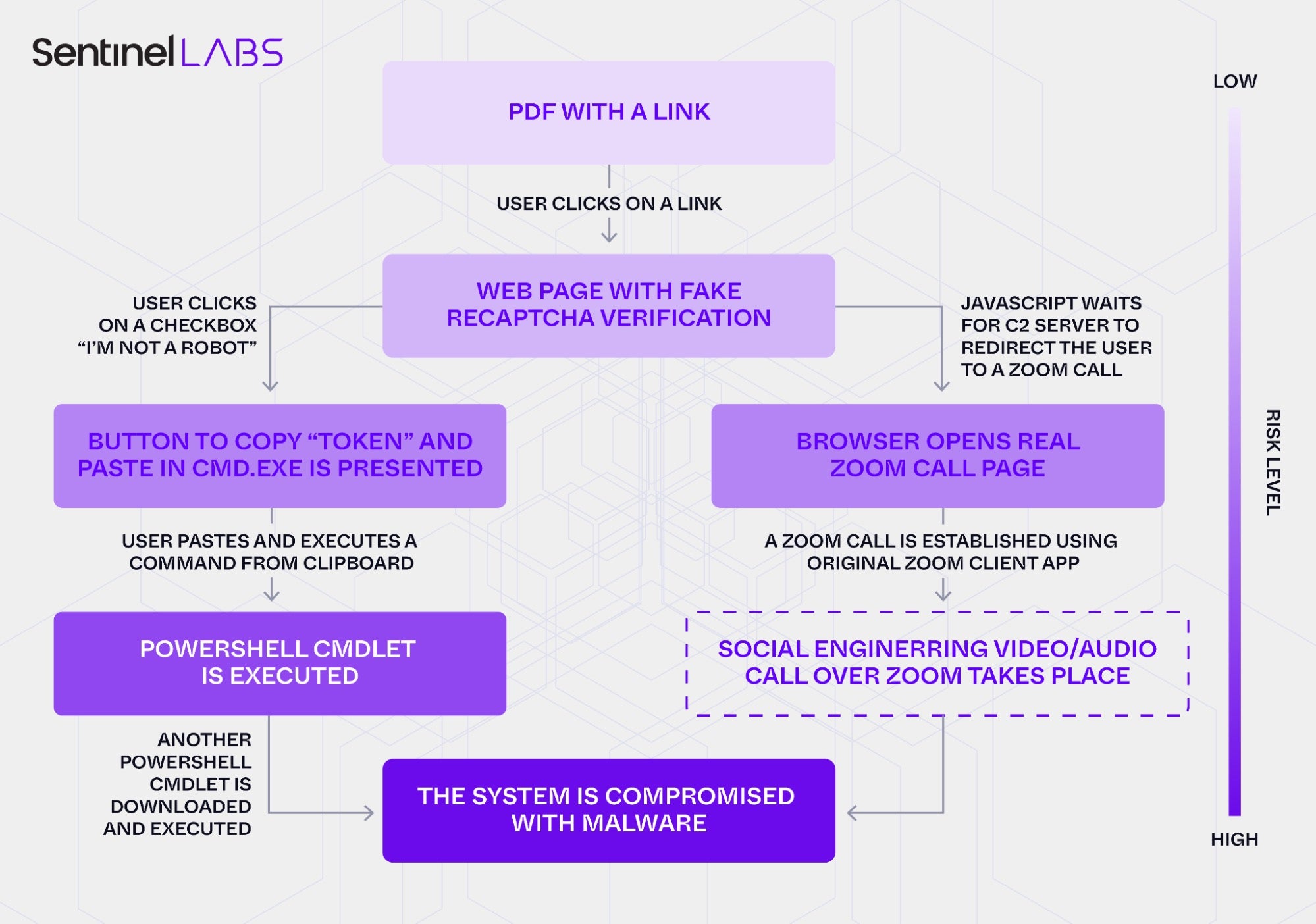
Once running, the script deployed a multi-stage PowerShell payload leading to a WebSocket remote access trojan (RAT) hosted on Russian-owned infrastructure. The RAT enables arbitrary command execution, data exfiltration, and the potential deployment of further malware through encrypted WebSocket communications. Although investigations show that the attackers spent six months preparing the campaign, it remained active for only 24 hours, pointing to an infrastructure that demonstrates sophisticated operational security and planning.
SentinelLABS linked the campaign to an additional Android-based espionage effort hosted on princess-mens[.]click, which distributes spyware-laden APKs disguised as adult entertainment or cloud storage apps designed to harvest contacts, media files, and geolocation data.
While attribution remains unconfirmed, technical overlaps, including the ClickFix lure and Russian-hosted C2s, suggest possible ties to COLDRIVER (aka UNC4057 or Star Blizzard), a threat group linked to Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB). PhantomCaptcha is an example of a highly organized and adaptive adversary, able to blend social engineering, short-lived but highly compartmentalized infrastructure, and cross-platform espionage to target Ukraine’s humanitarian and government sectors.